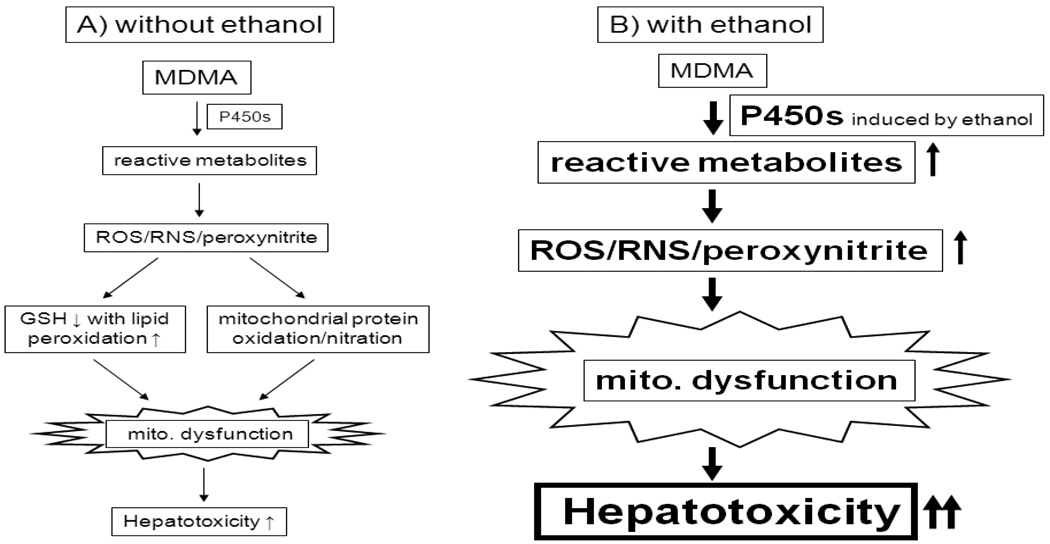
Fig. 3.
Synergistic interaction between MDMA and alcohol (or other abused drugs). MDMA, alcohol, or cocaine is known to decrease GSH levels, facilitating increased oxidative stress. Ethanol (or cocaine) increases some P450 isozymes involved in MDMA metabolism, leading to greater production of MDMA metabolites with decreased levels of cellular antioxidants, contributing to increased oxidative/nitrosative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and sensitivity toward MDMA-mediated tissue damage, as exemplified with hepatotoxicity.