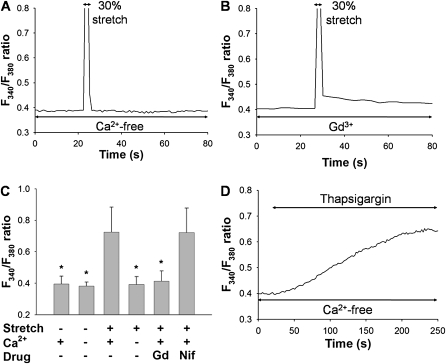
Figure 3.
Roles of Ca2+ influx from extracellular side in F340/F380 signals after a mechanical stretch equivalent to 30% strain. Representative traces of changes in F340/F380 ratio in a Ca2+-free solution (A) and in the presence of 10 μM Gd3+, a stretch-activated cation channel inhibitor (B). (C) Effects of extracellular Ca2+, 10 μM Gd3+, or 10 μM nifedipine (Nif) on levels of F340/F380 ratio in response to 30% mechanical stretch. Extracellular medium contains either 2 mM (normal solution) or 0 mM (Ca2+-free solution) of Ca2+. Bars represent means ± SD (n = 6). *Significantly different from values corresponding to stretched condition in normal solution (P < 0.001; one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni test). (D) Representative trace of F340/F380 ratio after application of 1 μM thapsigargin in Ca2+-free solution.