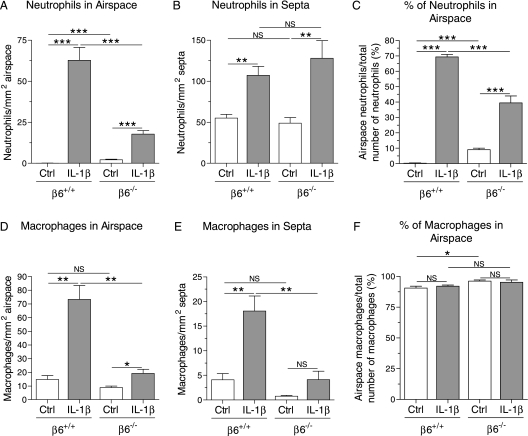
Figure 3.
Neutrophils and macrophages in the lungs of infant mice. Dams received doxycycline from the beginning of pregnancy until the pups were killed at PN7. Neutrophils and macrophages were detected by immunohistochemistry and counted in the alveolar airspaces and alveolar septal walls in five to six animals per group. (A) The number of neutrophils in the alveolar airspaces was higher in IL-1β/β6+/+ mice than in IL-1β/β6−/− mice. The number of cells is expressed per square millimeter of airspace area. (B) IL-1β increased the number of neutrophils in the alveolar septa in both β6+/+ and β6−/− mice. The number of cells is expressed per square millimeter of alveolar septal area. (C) The distribution of neutrophils between the alveolar lumen and the alveolar walls was different in IL-1β/β6+/+ and IL-1β/β6−/− mice. Most of the neutrophils in IL-1β/β6+/+ mice and IL-1β/β6−/− mice were in the alveolar lumen and alveolar walls, respectively. The IL-1β–induced infiltration of macrophages to the alveolar spaces (D) and alveolar walls (E) was decreased in β6−/− mice. The number of macrophages is expressed per square millimeter of distal airspace (D) and septal area (E). (F) The majority of macrophages was found in the alveolar spaces in all groups of mice. Data are presented as means (±SEM). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.