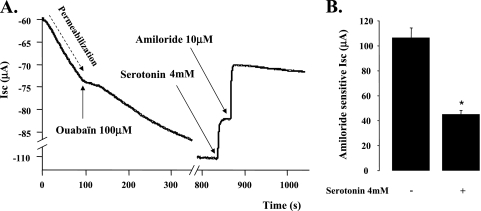
Figure 4.
5-HT–induced inhibition of the amiloride senitive Na+ transport across primary cultures of polarized rat ATII cell monolayers is not mediated through the Na+/K+ ATPase. (A) Neither the kinetic of the 5-HT–mediated inhibition nor the magnitude of 5-HT effect was affected by the Na+/K+ ATPase blockade and basolateral membrane permeabilization. Permeabilization was achieved with nystatin (400 μg/ml) in the basolateral chamber. All experiments were performed under asymmetric conditions with different saline solutions for apical and basolateral chambers (apical: 140 mM NaCl, 4 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM CaCl2, 10 mM Hepes, and 15 mM glucose [pH = 7.3, adjusted with NaOH]; basolateral: 10 mM NaCl, 130 mM N-methyl-D-glucamine, 4 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM CaCl2, 10 mM Hepes, and 15 mM glucose [pH = 7.3, adjusted with HCl). The EasyMount system was used for all experiments. The voltage was clamped at 0 mV during the whole experiments. (B) This histogram summarizes the effect of 5-HT after Na+/K+ ATPase inhibition and permeabilization of the basolateral membrane of ATII cell monolayers. The results are means (±SD) of four independent experiments; *P < 0.05 from controls.