Figure 2. Cell-type specific expression of Apc in mouse lung.
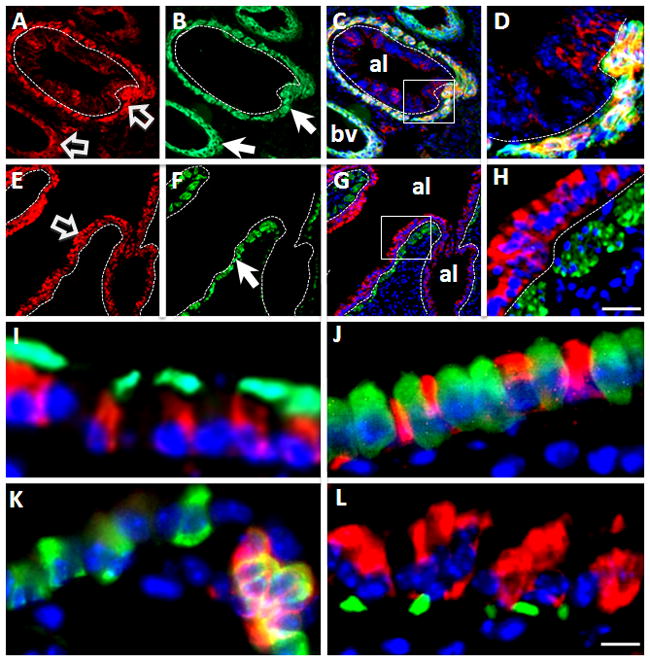
(A–H) Double immunofluorescent staining of Apc (red) and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA, green). (A–D) In E15.5 lung, Apc (red, panel A) and α-SMA (green, panel B) are co-localized in mesenchymal (smooth muscle) cells around large airway and blood vessels. Block arrows indicate Apc signal and arrows indicate α-SMA signal. High magnification of boxed area in merged image (panel C) is shown in panel D. (E–H) In adult lung, Apc is highly expressed in airway epithelial cells (block arrow), but weakly in smooth muscle cells as labeled by α-SMA staining (arrow, panel F). High magnification of boxed area of merged image (panel G) is shown in panel H. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Dotted lines outline airway basement membrane. Scale bar, 30μm for Panels A–C and Panels E–G; 10μm for Panels D&H.
(I–L). Cell type specific expression of Apc in airway epithelium of adult lung. (I) Double immunofluorescent staining of Apc (red) and β-tubulin IV (green). (J) Double immunofluorescent staining of Apc (red) and CC10 (green). (K) Double immunofluorescent staining of Apc (green) and PGP9.5 (red). (L) Double immunofluorescent staining of Apc (red) and P63 (green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Note that Apc co-localizes with β-tubulin IV (panel I) and PGP9.5 (panel K). Scale bar, 10μm.
