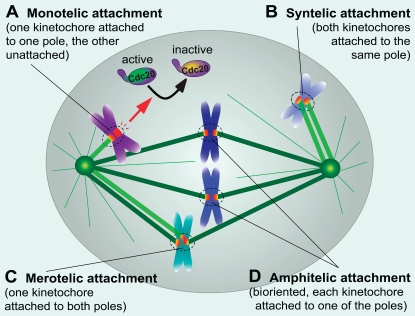
Figure 1.
Microtubule–kinetochore attachments. Four types of kinetochore–microtubule attachments are highlighted. (A) Monotelic attachment with only one kinetochore attached. Unattached kinetochores produce the mitotic checkpoint inhibitor that delays advance to anaphase by inactivating Cdc20, an activator of the ubiquitin ligase APC/C. (B) Syntelic attachment with both kinetochores attached to microtubules from the same pole. (C) Merotelic attachment with one kinetochore attached to microtubules from both poles. (D) Bioriented attachment (also known as amphitelic) with the two kinetochores of each chromatid pair attached to opposite spindle poles.