Figure 1. STAT1 deletion attenuated the expression of IFN-γ-responsive genes in transgenic mice expressing IFN-γ in the CNS.
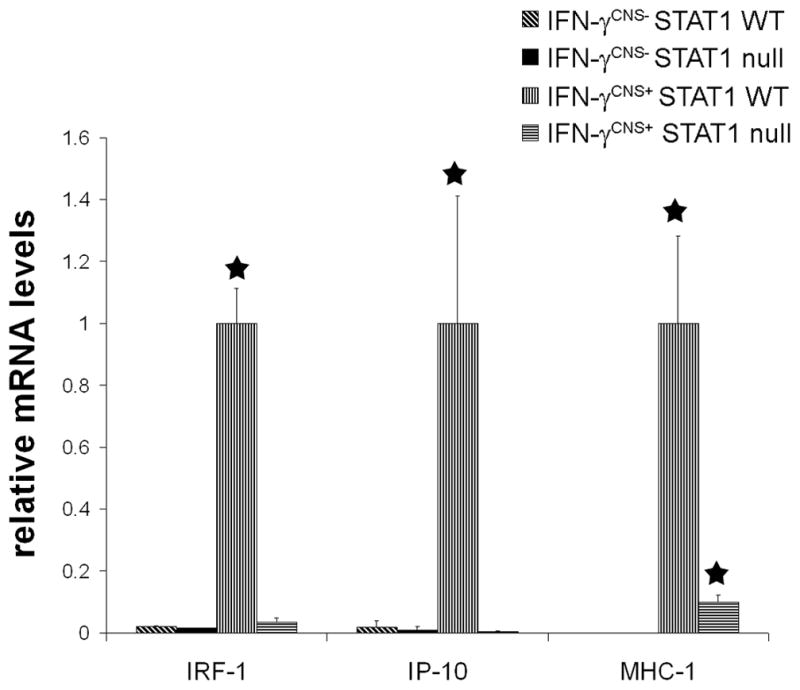
Real-time PCR analysis revealed that the presence of IFN-γ significantly increased the levels of IRF-1, IP-10 and MHC-1 mRNAs in the brain of 21-day-old mice on a STAT1 wild type background. The increased expression of STAT1-dependent, IFN-γ-responsive genes IRF-1 and IP-10 was abolished in the brain of IFN-γ-expressing mice on a STAT1 null background. Nevertheless, the level of MHC-1 mRNA in the brain of IFN-γ-expressing mice on a STAT1 null background was significantly elevated compared to control IFN-γCNS−;STAT1 WT mice or IFN-γCNS−; STAT1 null mice. mRNA levels are relative to the housekeeping gene GAPDH. N = 3 animals, error bars represent standard deviation, asterisk p < 0.05.
