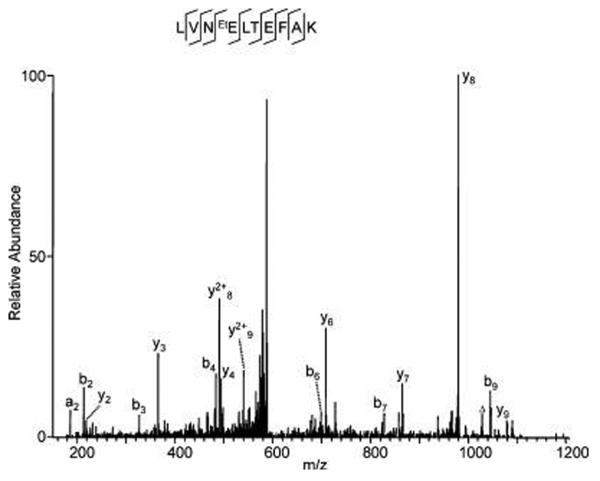
Figure 1.
Identification of ethylated glutamate in BSA. BSA (~300 ng) was resolved by SDS-PAGE and stained with colloidal Coomassie staining solution composed of 9 vol of G−250 stain solution (ProtoBlue, National Diagnostics, Atlanta, GA) and 1 vol of ethanol. The BSA protein band was destained with water and washed with a buffer containing acetic acid/ethanol/water (10: 50:40, v/v/v) before in-gel digestion and analysis by HPLC/MS/ MS. The labels “b” and “y” designate the N- and C-terminal fragment ions, respectively, of the peptide produced by breakage at the peptide bond in the mass spectrometer. The label “a” designates N-terminal fragments produced by breakage at the C-C bond adjacent to the peptide bond. The number represents the number of N- or C-terminal residues present in the peptide fragment. The label “Δ” designates “b”, “y” or “a” ions with water and/or ammonia loss. The same nomenclature system is used for all subsequent figures.