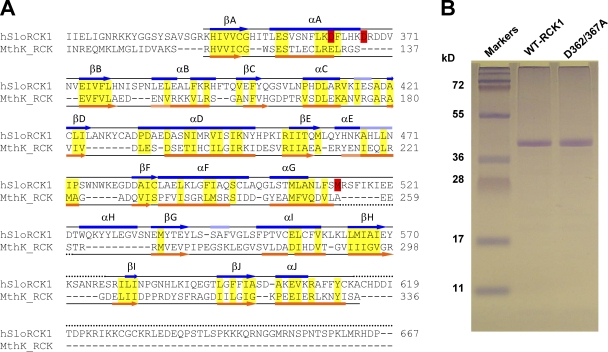
Figure 1.
Purification of the RCK1 domain of the human BKCa channel. (A) Structure-based sequence alignment of the BKCa channel (GI, 507922) C terminus (encompassing the RCK1 domain) with the MthK (GI, 2622639) RCK domain. The α helices are depicted as bars, and β strands are shown as arrows. The secondary structures (obtained from the DSSP reference set) above the sequences (blue) are obtained from the atomic structure of the BKCa C-terminal domain (Protein Data Bank accession no. 3MT5) (Yuan et al., 2010) and below the sequences (orange) are obtained from the atomic structure of the MthK RCK domain (Protein Data Bank accession no. 2AEF) (Dong et al., 2005). Light blue and light orange bars correspond to 310 helices. Dotted lines are unresolved regions in the respective crystal structures. Semi-conserved residues within ordered structures are highlighted yellow. Residues known to be involved in high-affinity Ca2+ sensitivity in the BKCa RCK1 domain (D362/D367 and M513) are highlighted red. (B) 12.5% SDS-PAGE of purified WT-RCK1 and D362/367A-RCK1 stained with Coomassie blue. Both proteins migrate as an ∼40-kD band, consistent with their expected mol wt (41 kD).