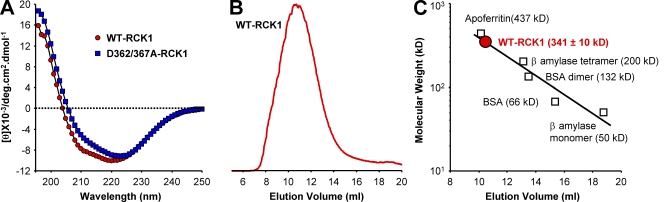
Figure 2.
Structural analysis of WT and D362/367A RCK1. (A) Far-UV CD spectra of WT-RCK1 and D362/367A-RCK1 domains obtained in nominal free [Ca2+] (0.00058 µM). The CD spectrum of WT-RCK1 exhibits a strong signal at 220 nm, whereas D362/367A displays different spectral properties with a red-shifted minimum at 223 nm (relative to WT-RCK1), suggesting that the double D362/367A mutation altered its secondary structure. (B) Characteristic size-exclusion column profile of the purified WT-RCK1 domain reveals an elution peak at ∼10.5 ml. (C) A calibration curve is established by plotting the log (mol wt) of proteins with known mol wt versus their elution peak (R2 = 0.91). The purified WT-RCK1 domain is calculated to elute with an apparent mol wt of 341 ± 10.0 kD (n = 7), suggesting a homo-octameric assembly of RCK1 domains (theoretical octameric mol wt = 328 kD).