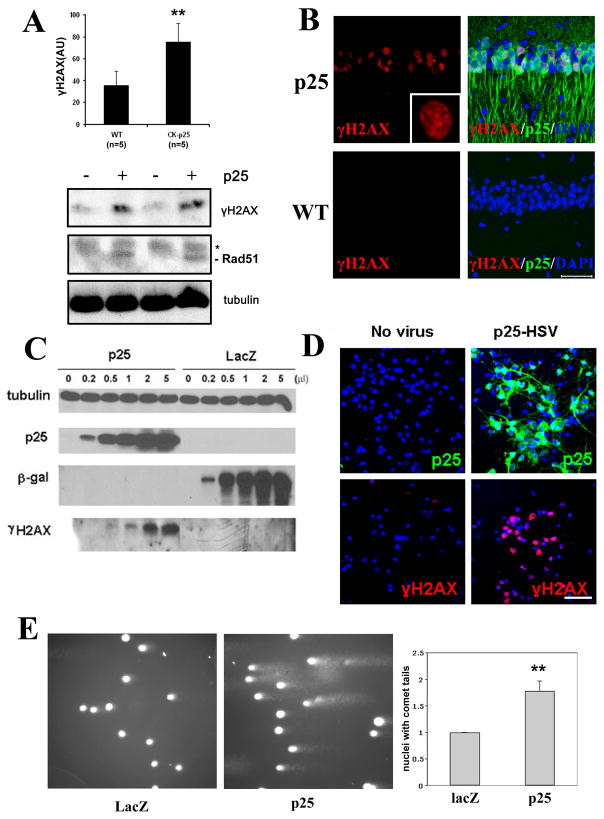
Figure 2. Double-strand DNA damage occurs following p25 induction.
(A) Western blots from induced CK-p25 mice forebrain lysates show increased levels of γH2AX and Rad51 compared to WT controls. Asterisk indicates nonspecific band. Quantification of γH2AX levels (±S.D.) from multiple WT controls (n=5) and CK-p25 mice (n=5) induced between 2 and 12 weeks are shown in top panel. (B) Staining of vibratome sections with γH2AX reveals immunoreactivity specifically in the nuclei of p25-GFP-expressing neurons in two-week induced CK-p25 mice (top panels) but not in neurons of WT controls (bottom panels). CA1 region is shown. Inset is a magnification of γH2AX signal showing punctate nuclear staining. Scale bar = 50μM. (C) Primary cortical neurons were infected with increasing titers of herpesvirus expressing p25 (p25-HSV) or lacZ-HSV control and analyzed for γH2AX levels by Western blot. (D) Primary cortical neurons infected with p25-HSV and fixed 8 hours post-infection display robust immunoreactivity with γH2AX (right panels), compared to control uninfected neurons (left panels). p25 overexpression was verified with p35 antibody (top panels). Top and bottom panels are from different fields. (E) Comet assays were carried out on primary neurons infected with p25-HSV or lacZ-HSV for 10 hours. Representative micrographs of comet assay fields are shown in the left and middle panels for p25-HSV infected and lacZ-HSV infected neurons, respectively. Comet tails indicate DNA with breaks, resulting in increased migration towards the direction of the current (left to right). Right panel shows quantification of the percentage of neurons with comet tails from three separate experiments. Results are displayed as fold change to control (lacZ-HSV infected) neurons. P-values (**p<0.005) were calculated from multiple experiments by two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test.