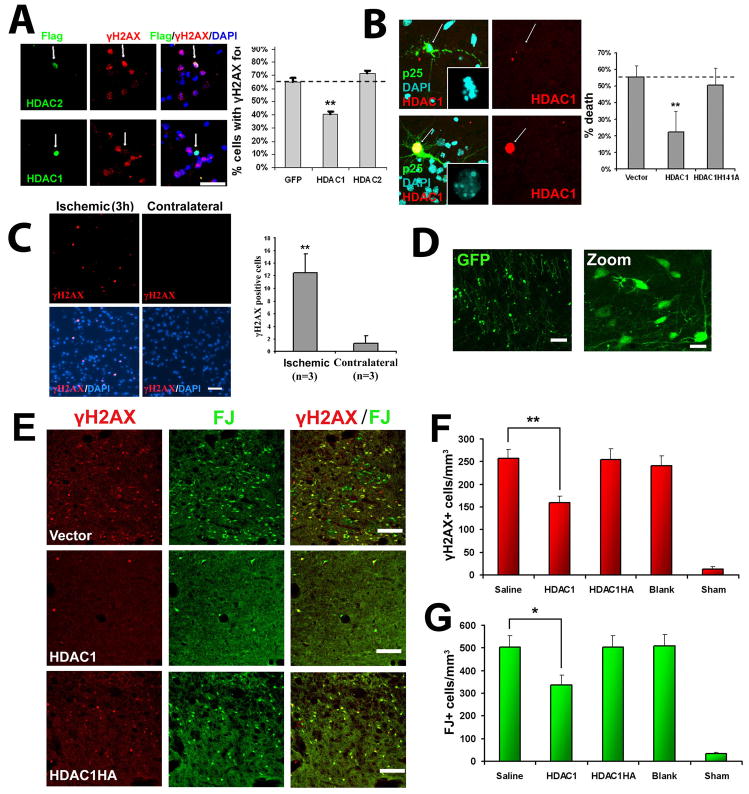
Figure 6. HDAC1 gain-of-function rescues against p25-mediated double-strand DNA breaks and neurotoxicity.
(A) Overexpression of HDAC1 rescues against p25 mediated formation of γH2AX. Primary cortical neurons were transfected with vector, HDAC1, or HDAC2 as described. At 12 hours posttransfection, neurons were infected with p25-HSV virus, fixed after 8 hours, and immunostained for γH2AX. HDAC-positive cells were scored for immunoreactivity towards γH2AX. (B) Overexpresson of HDAC1 rescues against p25-mediated neurotoxicity. Primary cortical were transfected with p25-GFP plus blank vector, flag-HDAC1, or catalytic dead flag-HDAC1-H141A mutant. At 24h posttransfection, cells were fixed and immunostained for flag. p25 transfected cells and p25/HDAC1 transfected cells were scored for cell death based on nuclear condensation and neuritic integrity as described. For (A) and (B), averages from multiple experiments ±S.D. are shown. Representative micrographs for HDAC1 are shown on left panels. Arrows indicate p25-positive neurons expressing or not expressing HDAC1. P-values (HDAC1 vs control, **p<0.005) were calculated from multiple experiments by two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test. Bar= 50 μM. (C) Adult Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to unilateral middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) as described. Paraffin sections from brains fixed at three hours post-MCAO show γH2AX immunoreactivity specifically within the ischemic area (left panels) but not in the contralateral area (right panels). Images are representative of multiple animals. Average numbers of γH2AX-positive cells per field (field diameter ~900μm) from multiple experiments ±S.D. are displayed. 20 fields were counted per experiment. P-values (**p<0.005) were calculated from multiple experiments by two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test. (D) Injection of blank vector (expressing GFP) into striatum results in efficient and widespread expression in striatal neurons. Injection of virus into the striatum of adult Sprague-Dawley rats was followed examination of GFP expression after 24 hours. Left pane bar = 100μM, right panel bar = 30μM. (E) HDAC1 expression protects against ischemia-induced neuronal death and γH2AX formation in vivo. Adult Sprague-Dawley rats were injected with virus in the striatum, subjected to bilateral transient forebrain ischemia after 24 hours, then examined 6 days later for Fluoro-Jade and γH2AX staining as described. Representative images from mice injected with HSV-HDAC1, HSV-HDAC1H141A, and blank HSV (Vector) are shown. Scale bar = 100μM. (F) Quantification of γH2AX+ cells from mice injected with saline, HSV-HDAC1, HSV-HDAC1H141A, vector, or mice subjected to sham procedure are shown. (G) Quantification of FJ+ cells from the same mice as (F). For (F) and (G), Data is presented as Mean ± SEM. P-values (*p<0.05; **p<0.005) were calculated from multiple experiments by two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test. Bar = 100μM.