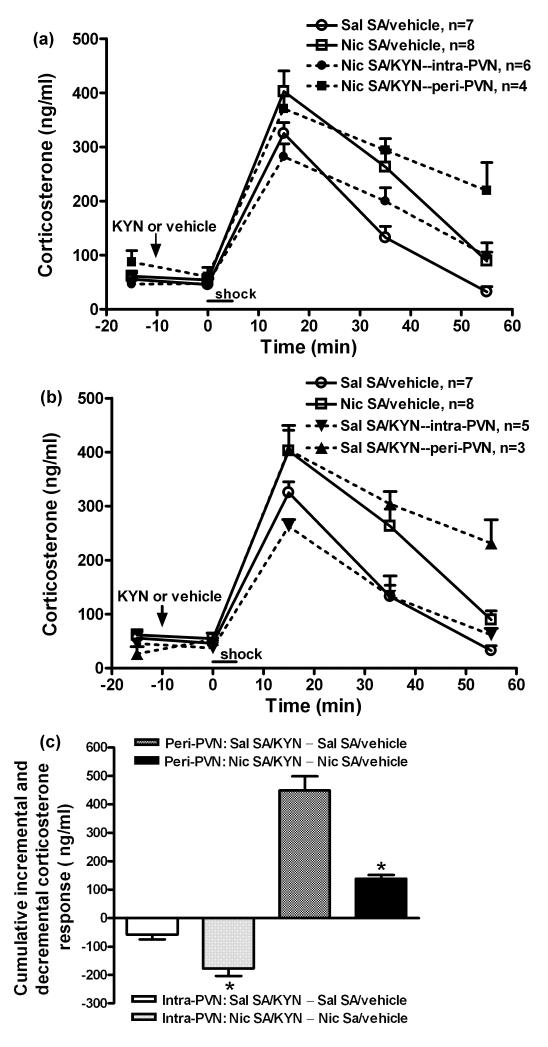
Fig. 4.
The effects of intra- and peri-PVN kynurenic acid (KYN) on overall corticosterone responses (panels a, b) and incremental or decremental changes (c) in corticosterone secretion induced by mild footshock stress during nicotine (Nic) and saline (Sal) self-administration (SA). Kynurenic acid, an ionotropic glutamate receptors antagonist, (1.5 nmol/side) was bilaterally microinjected into PVN 10 min prior to footshock. Corticosterone levels were increased by footshock (factorial ANOVA: time, p < 0.001); the increase was greater in rats self-administering nicotine (SA group, p < 0.01), and also was affected by kynurenic acid (PVN treatment, p < 0.01; time × PVN treatment, p < 0.01) depending on the injection site (site, p < 0.001; time × site, p < 0.001). The differential effects of intra- vs. peri-PVN microinjections of kynurenic acid in the Nic and Sal SA groups were delineated by graphing them separately. Both panels contain the same data from the groups pretreated with vehicle. Panel (a): Intra-PVN kynurenic acid completely blocked the enhanced corticosterone response in the nicotine group (two-way ANOVA: Nic SA/vehicle vs. Nic SA/KYN--intra-PVN, p < 0.05). In contrast, peri-PVN kynurenic acid was ineffective (p > 0.05). Panel (b): peri-PVN kynurenic acid augmented the corticosterone response in the saline group (two-way ANOVA: Sal SA/vehicle vs. Sal SA/KYN--peri-PVN, p < 0.001). A main effect of intra-PVN kynurenic acid was not detected (p > 0.05). Analysis of peak corticosterone levels (15 min) did indicate a 20% reduction in the Sal SA/KYN--intra-PVN vs. Sal SA/vehicle (p < 0.05, t-test). Panel (c): Intra-PVN kynurenic acid induced a significantly greater cumulative (across time) decrement in footshock-induced corticosterone secretion in the nicotine SA group compared to saline controls; conversely, peri-PVN kynurenic acid induced a significantly greater cumulative increment in footshock-induced corticosterone secretion in saline SA group compared to the nicotine group. *, p <0.05, for cumulative change in nicotine vs. saline groups after intra- or peri-PVN kynurenic acid (t-test).