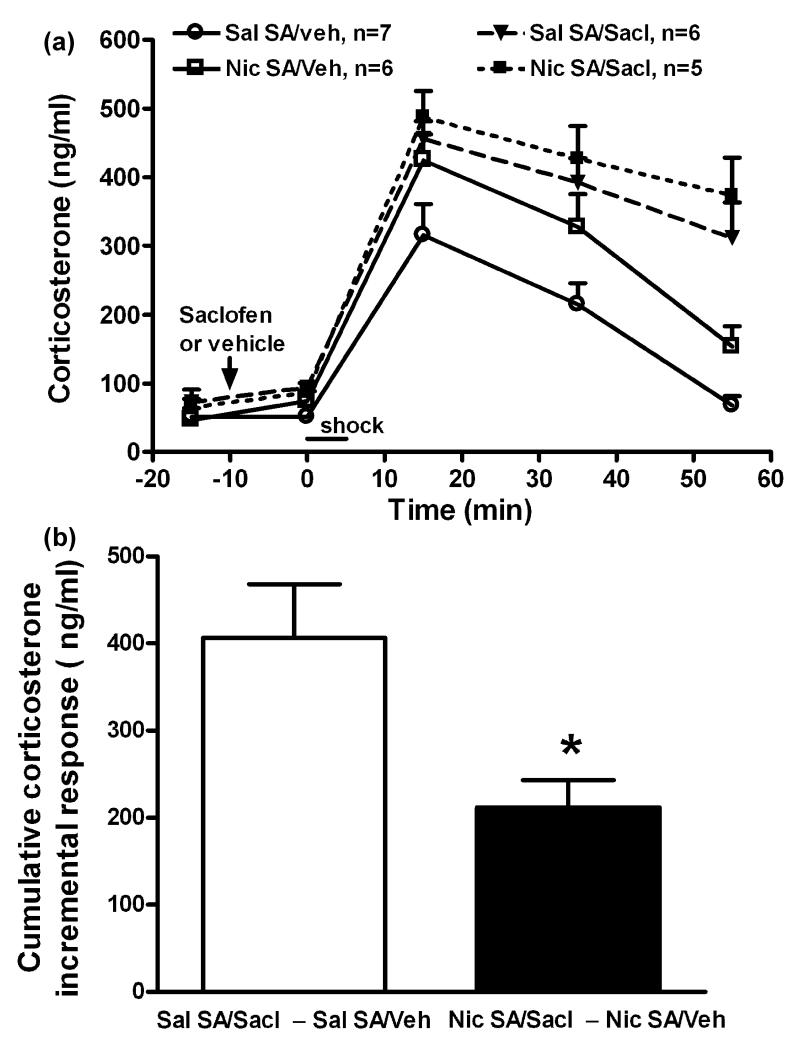
Fig. 6.
The effects of saclofen on overall corticosterone responses (panel a) and the increment in corticosterone secretion (b) induced by mild footshock stress during chronic nicotine (Nic) vs. saline (Sal) self-administration (SA). Saclofen (Sacl, GABA-B receptor antagonist, 10 pmol/side) was bilaterally microinjected intra-PVN. Panel (a): Corticosterone levels were increased by footshock (factorial ANOVA: time, p < 0.001), and the elevation was greater in rats self-administering nicotine (SA group, p < 0.01; time × SA group, p > 0.05), and also greater in all saclofen pretreated rats in both the nicotine and saline SA groups (PVN treatment, p < 0.001; time × PVN treatment, p < 0.001). Panel (b): In saline SA groups, saclofen enabled a significantly greater cumulative incremental corticosterone response to footshock than in the nicotine SA groups. *, p < 0.05 (t-test).