Fig. 2.
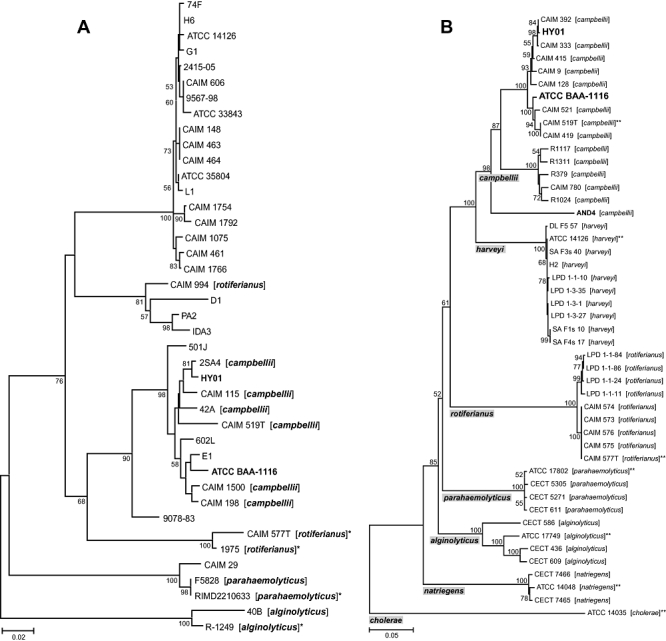
Multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) of Harveyi clade members. A. Phylogenetic tree based on the Neighbour-Joining method using concatenated sequences from the ftsZ, mreB and topA genes (1528 nt) and MEGA software v4.0. Original species designations are in brackets. Strains lacking species designations were originally identified as V. harveyi. This analysis includes all of the strains used in the CGH analyses (with the exception of strain 50A) and four additional strains that are denoted with an asterisk ‘*’. The primary sequence information has been submitted to the GenBank database and the relevant accession numbers can be found in Table S1. B. Phylogenetic tree based on the Neighbour-Joining method using concatenated sequences from the rpoD, rctB and toxR genes (1848 nt) and MEGA software v4.0. Strain identifiers ending in ‘**’ denote type strains. With the exception of BAA-1116, HY01 and AND4 (bold type), all sequences used in this MLSA were downloaded from the ‘Taxonomy of the Vibrios’ database (http://www.taxvibrio.lncc.br/). Alignments for both analyses were generated using the clustalw program and bootstrap percentages > 50% from 1000 simulations are shown to the left of each branch point. The scale bar represents the number of substitutions per site.
