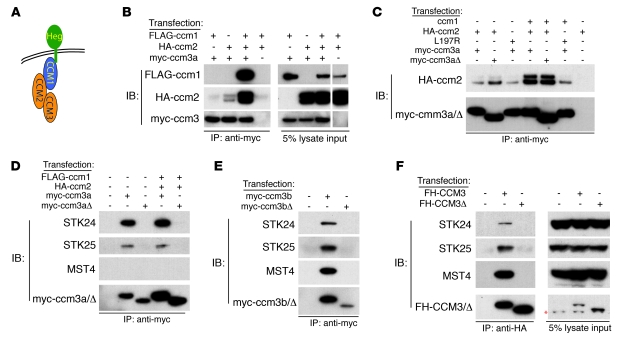
Figure 3. ccm3Δ proteins form a complex with ccm1 and ccm2 but fail to bind the GCK-III family of sterile 20–like kinases.
(A) A working model in which HEG receptors bind CCM1, CCM1 binds CCM2, and CCM2 binds CCM3 is shown. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation of a zebrafish ccm1/ccm2/ccm3 protein complex. FLAG-ccm1, HA-ccm2, and myc-ccm3 were coexpressed and ccm3 immunoprecipitations performed (left). Protein expression is shown by immunoblot analysis (right). The white line indicates the boundary of a noncontiguous lane run on the same gel. (C) Formation of the zebrafish ccm1/ccm2/ccm3a complex requires the ccm2 PTB domain but not the 18 amino acids encoded by ccm3 exon 3. ccm proteins were coexpressed and ccm3 immunoprecipitations performed. ccm2L197R contains a point mutation in the PTB domain that blocks interaction with ccm1 (10). ccm3aΔ proteins lack the 18 amino acids encoded by exon 3. (D) Zebrafish ccm3a interaction with STK24 and STK25 requires the 18 amino acids encoded by exon 3. ccm3 immunoprecipitations were performed as described above, and co-immunoprecipitated endogenous human STK24, STK25, and MST4 were detected with specific antibodies. (E) Zebrafish ccm3b interaction with STK24, STK25, and MST4 requires the 18 amino acids encoded by exon 3. (F) Human CCM3 interaction with STK24, STK25, and MST4 requires the 18 amino acids encoded by exon 5. CCM3 and CCM3Δ double-tagged with Flag and HA (FH) were expressed and CCM3-STK co-immunoprecipitation experiments performed as described for D and E. The red asterisk indicates a background band present in all lanes.