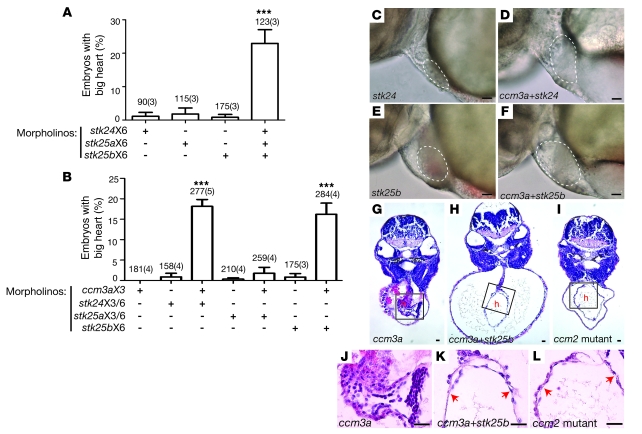
Figure 4. ccm3 and GCK-III family STKs interact in the CCM pathway in vivo.
(A) STK deficiency confers the big heart phenotype characteristic of CCM deficiency in zebrafish embryos. Conferral of the big heart phenotype was scored following injection of low-dose morpholinos targeting stk24 (stk24X6, 3 ng/embryo), stk25a (stk25aX6, 3 ng/embryo), stk25b (stk25bX6, 3 ng/embryo) alone or a combination of all 3 morpholinos. Shown are mean and SEM. The number of embryos examined is indicated above each bar, and the number of separate injections performed with the indicated morpholinos is indicated in parentheses. ***P < 0.001 by Student’s t test. (B) ccm3 and STKs functionally interact in the CCM pathway in zebrafish embryos. Low-dose morpholinos against ccm3a (ccm3aX3, 3 ng/embryo) and stk24 (stk24X3+stk24X6, 2 ng/embryo each), stk25a (stk25aX3+stk25aX6, 2 ng/embryo each) or stk25b (stk25bX6, 2 ng/embryo) were injected separately or in combination into wild-type embryos and the presence of the big heart phenotype characteristic of CCM signaling deficiency was scored at 48 hpf. ***P < 0.001 by Student’s t test. (C–F) Representative light microscopic images of the big heart phenotypes conferred by the morpholinos described in B. The atrial margins are outlined by white dashed lines. (G–I) Representative histologic cross sections of 48-hpf morphant (ccm3aX3 and ccm3aX3+stk25bX6) and mutant (ccm2) embryos stained with hematoxylin and eosin. h, heart. (J–L) High-power images of the boxed regions of hearts shown in G–I. Scale bars: 20 μm.