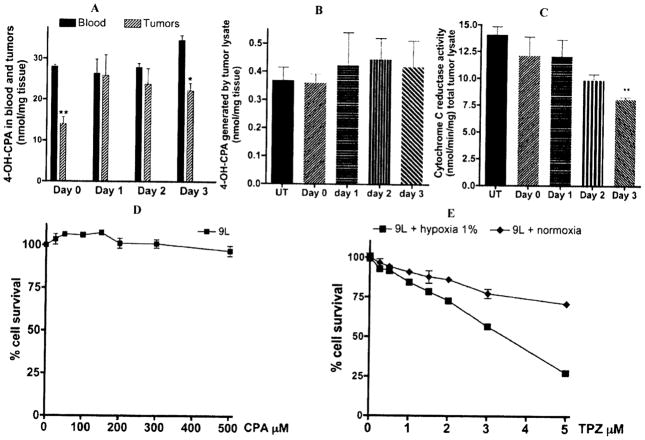
Fig. 2.
Rat 9L gliosarcoma tumors were grown in scid mice. When the tumor size reached 1 cm3, CPA was injected as a single dose at 140mg/Kg BW i.p. every 7 days (day 0 corresponds to 7 days after one CPA injection, and day 1, 2 or 3 correspond to 1, 2, or 3 days after the 2nd of two CPA injections). A, To assess drug entry in tumors after CPA treatment, the amount of 4-OH-CPA in the blood and tumors were measured in animals killed 15 min after injection of a small test dose of 50 mg/kg CPA i.p. at day 0, 1,2, and 3 after the second CPA injection. Cardiac blood and tumor homogenates (n=4 tumors) were processed to determine their content of activated CPA. *: p< 0.05 and **: p< 0.01. B, Activated CPA metabolite, CPA activation by tumor extracts was assayed as previously described [24]. C, P450 reductase activity was assayed using 20 μg of tumor extracts, lysed by sonication and then assayed for P450R-catalyzed, NADPH-dependent cytochrome C reduction (DA550) at 30°C. Cytotoxicity assays – Cells were plated in triplicate at 4000 cells/well of a 48-well plate 18–24 hr prior to drug treatment. D, Cells treated with CPA (0 to 500 μM) were incubated for 4 days under normoxia. E, Cells treated with TPZ (0 to 5 μM), were incubated for 4 days in a tissue culture incubator maintained under hypoxic conditions 1% O2, or under normoxic conditions 19.6% O2. Cell viability after this time was determined using a crystal violet/alcohol-extraction assay. Data are presented as cell number relative to drug-free controls, mean ± SD.