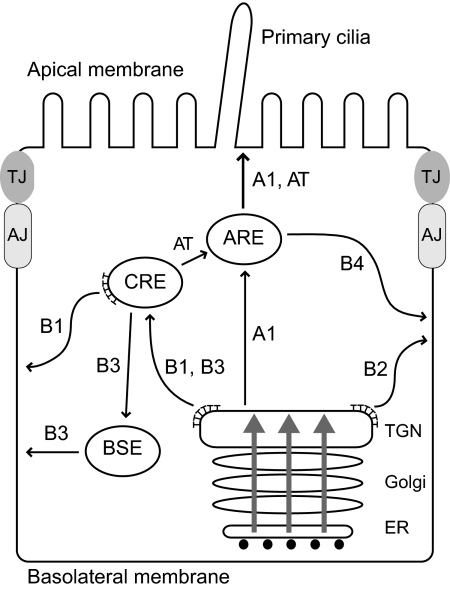
Figure 8.
The model depicts a variety of routes followed by newly synthesized EGFR in polarized renal cells. EGFRs are transported to the CRE where they undergo AP-1B–dependent transport to the basolateral membrane via route B1. EGFR also follows an AP-1B–independent pathway that may bypass CREs using a direct route from the TGN to the basolateral membrane (B2). Alternatively this pathway may involve a hypothetical route from CREs to BSEs (B3). Introduction of an aspartic acid residue for Thr654 unmasks a third route that traverses AREs en route to the basolateral membrane (B4). Receptors in this pathway may reach AREs by a direct route from the TGN (A1) or via a CRE intermediate (AT). The B1 pathway is impaired in μ1B-null LLCPK1 cells as well as cystic cells from the BPK model with constitutive μ1B expression. The B4 pathway bypasses AP-1B and reconstitutes polar EGFR expression in both cell types. Apically missorted EGFRs probably follows the N-glycan–dependent A1 pathway rather than the lipid raft–dependent pathway that involves ASE intermediates (not shown). Gray arrows indicate polarized protein cargoes that may be presorted in the ER or Golgi. AJ, adherens junction; TJ, tight junction; ⊤, clathrin.