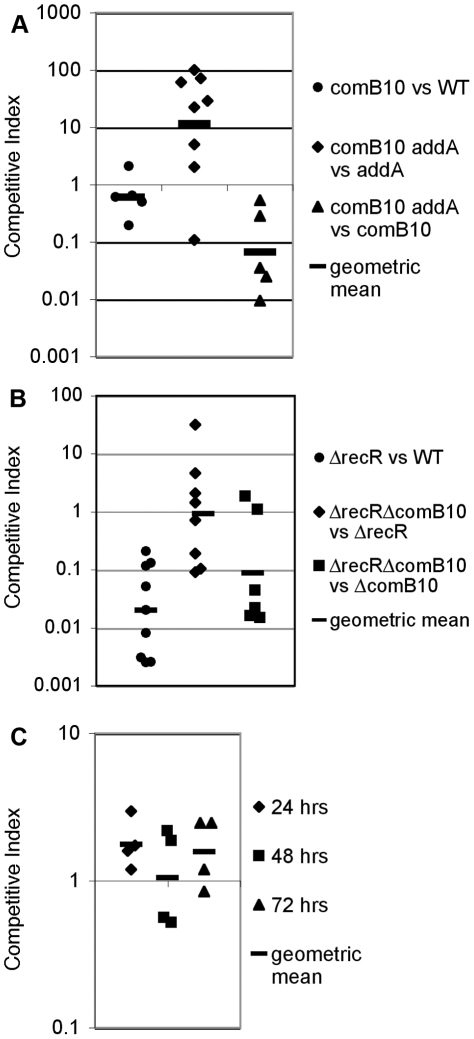
Figure 6. DNA damage responsive genes do not contribute to DNA repair during stomach colonization.
Each data point shows the competitive index of mutant cells vs wild-type cells or the indicated double mutant compared to either single mutant for a single mouse after one-week stomach colonization (A, B) or for a single well during co-culture in broth (C) and bars indicate the geometric mean. A. Competition between the ΔcomB10 mutant and wild-type cells shows no defect during stomach colonization; however stomach colonization of the ΔaddA mutant is improved by disruption of natural competence. B. Competition between the ΔrecR mutant and wild-type cells shows a strong defect during stomach colonization, but is unaffected by disruption of natural competence. C. Competence does not affect growth of the ΔaddA mutant in broth culture. The ΔaddA ΔcomB10 double mutant and the ΔaddA mutant were maintained in logarithmic growth for three days in broth culture by dilution.