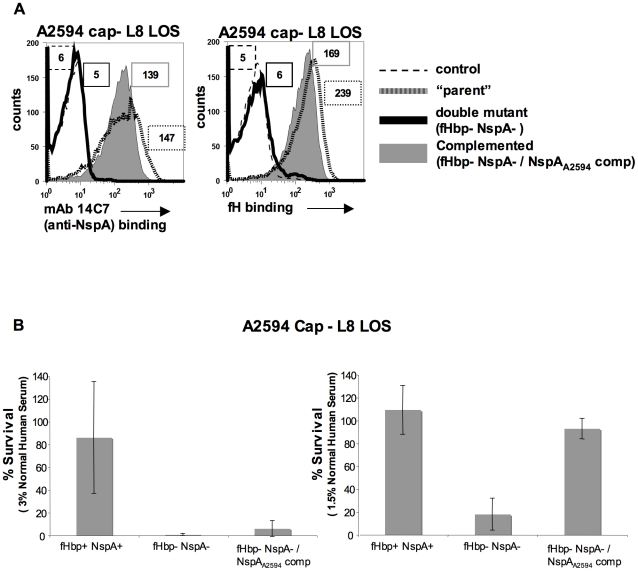
Figure 11. Complementation of fHbp NspA double mutants with NspA restores fH binding and serum resistance.
A. Meningococcal strain A2594 Cap−/L8 LOS (“parent”), its fHbp nspA double mutant (fHbp− NspA−) and its fHbp nspA double mutant complemented with NspA (fHbp− NspA−/NspAA2594 comp) were examined for their ability to bind to MAb 14C7 (anti-NspA) and to fH (20 µg/ml) by flow cytometry. The boxed numbers accompanying each histogram represents the median fluorescence of 14C7 or fH binding to the entire bacterial population. Controls (shown by the broken lines) represent fluorescence where either mAb 14C7 or fH or was omitted from the reaction mixture. Axes are as described for Figure 1A. B. Strain A2594 Cap−/L8 LOS (fHbp+ NspA+), its fHbp nspA double mutant (fHbp− NspA−) and its fHbp nspA double mutant complemented with NspA (fHbp− NspA−/NspAA2594 comp) were tested for their ability to resist killing by NHS at concentrations of 3% (left graph) or 1.5% (right graph) in a serum bactericidal assay. The y-axis represents percent survival. Error bars indicate standard deviation calculated from 3 independent experiments. With 1.5% NHS the decreased survival observed in strains that lack NspA was statistically significant (P<0.02 by a t-test) compared to the parent strain expressing both NspA and fHbp.