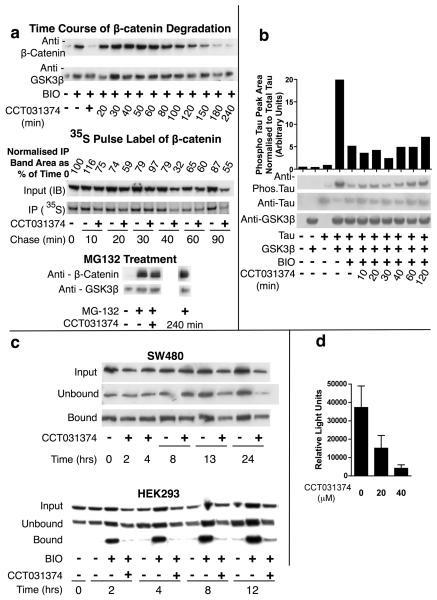
Fig 4. Mechanism of action of CCT031374.
a. CCT031374 and β-catenin degradation in mouse L-cells. Western blots and autoradiographs of lysates of mouse L-cells that were exposed to BIO (7.5μM) for 6h prior to addition of CCT031374 (20μM) in the presence of BIO for the times shown. CCT031374 (20μM) increased turnover of 35S-pulse labelled β-catenin. BIO (7.5μM) was present throughout labelling and chase periods. Western blots of lysates from mouse L-cells after 240min of treatment with 20μM CCT031374 after 6 hours of 50μM MG132 proteasomal inhibitor or 6 hours of coincubation of CCT031374 with 50μM MG132 (+). b. CCT031374 does not prevent BIO's inhibition of Tau phosphorylation by GSK3. Western blots of lysates from HEK293 cells that had been transfected with expression plasmids for Tau and GSK3β as indicated and had been treated with BIO (7.5μM) for 4h or with both BIO and CCT031374 (20μM) for the indicated time periods. Relative phosphorylated: total Tau levels were quantified. c. CCT031374 decreased ‘free’ β-catenin levels in HEK293 cells but not in SW480 cells. ‘Free’ β-catenin was isolated from cell lysates by pull down with a GST-E-cadherin fusion protein. d. CCT031374 treatment of SW480 cells decreased TCF-dependent transcription of Topflash luciferase reporter. SW480 cells were transfected with Topflash reporter, then exposed to compound for 24h. Reporter activity was normalised to co-transfected TK-renilla luciferase activity.