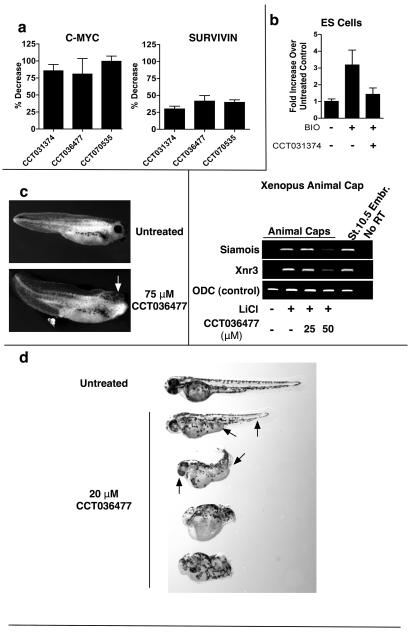
Fig 5. Effect of compounds on Wnt target gene expression and development.
a. HEK293 cells were transfected with CMYC-luc or SURVIVIN-luc promoter-reporter constructs together with Axin-GID inducer and exposed to 40μM compound for 24h. Reporter activity was normalised to expression from a co-transfected CMV-lacZ reporter. b. CCT031374, at 20 μmol/L, repressed BIO-induced LEF1 expression in human neurogenic embryoid bodies exposed to 3 μmol/L BIO and CCT031374 for 24 h. The relative abundance of LEF1 was normalized to ACTB. CCT036477 decreased Siamois and Xnr3 expression in Xenopus animal cap assays. Animal caps were treated with 0.3 mol/L LiCl for 10 min, then incubated in medium with or without CCT036477 for 3 h. RNA from NF stage 10.5 embryos provided a second positive control.
c. CCT036477 inhibited the development of Xenopus anterior head structures such as the eye (indicated with an arrow) and the cement gland. Embryos were exposed to DMSO or 75μM CCT036477 from the 4-16 cell stage to NF stage 38. d. CCT036477 induced head and tail patterning defects (indicated with arrows) in Zebrafish embryos. Zebrafish embryos were exposed to 1% DMSO or 20μM CCT036477 from fertilisation until mid-gastrulation. A range of mild to severe head patterning and tail patterning phenotypes were seen.