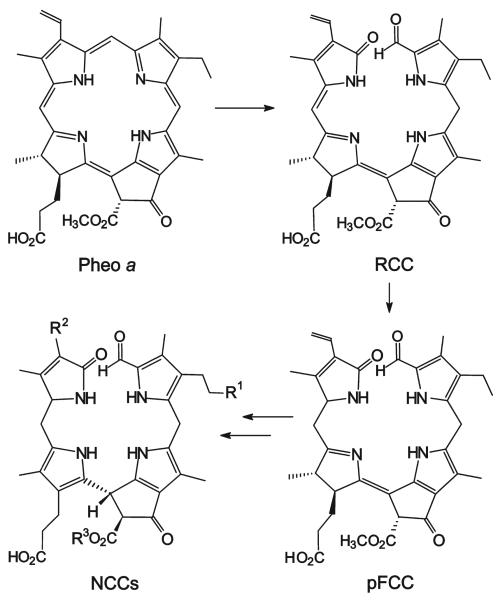
Scheme 1.
Outline of chlorophyll breakdown in senescent leaves.[11] The chlorophylls are degraded via pheophorbide a (Pheo a), “red” chlorophyll catabolite (RCC), and primary “fluorescent” chlorophyll catabolite (pFCC) to the “nonfluorescent” chlorophyll catabolites (NCCs, in which, typically, the residues R1, R2, and R3 vary).[11,13-15]