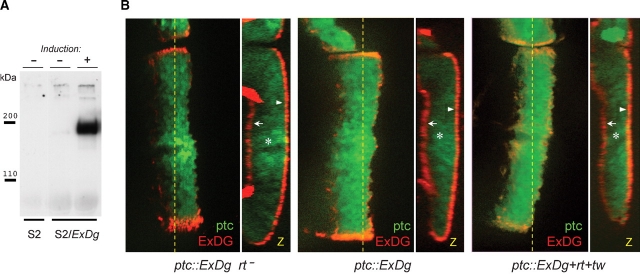
Fig. 2.
Secretion and subcellular localization of the ExDG protein. (A) Anti-FLAG Western blot of tissue culture media from S2 cells (control) or from S2 cells transfected with ExDG-expressing construct (with or without induction of expression). The results show that ExDG is efficiently secreted in a diffusible form outside of the cell. (B) Expression of ExDG in the third instar larval wing imaginal disks with a patched-GAL4 driver using the UAS-GAL4 system. Genotype of the disks: left disk (ptc::ExDg rt−) – ptc-GAL4 UAS-GFP/UAS-ExDg; rtP/rt2; middle disk (ptc::ExDg) – ptc-GAL4 UAS-GFP/+; UAS-ExDg/+; right disk (ptc::ExDg+rt+tw) – ptc-GAL4 UAS-GFP/UAS-rt UAS-tw; UAS-ExDg/+. ExDG expression is detected by immunofluorescent staining (red), while GFP signal (green) highlights the pattern of the ptc driver. Yellow dashed line indicates the position of Z cross-sections reconstructed for each disk in panel Z. Z cross-sections: no accumulation of the ExDG protein can be detected inside the columnar epithelium cells (asterisks), while the protein is efficiently delivered to the basal (arrows) or apical (arrowheads) surfaces of the disk epithelium. There is no significant difference in the subcellular localization of ExDG between the three genotypes. For all panels: dorsal is to the top; for the frontal-view sections: anterior is to the left; for Z cross-sections: basal is to the left.