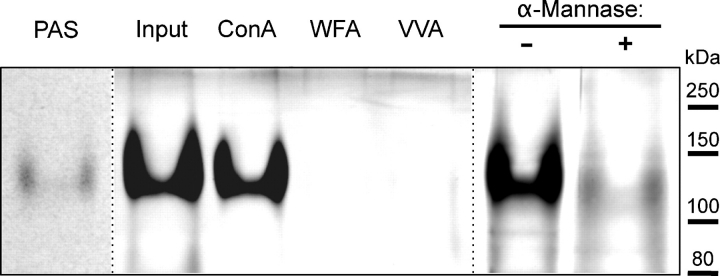
Fig. 8.
Analysis of trypsin-digested ExDG. Trypsin digestion of ExDG purified from RT-TW coexpression generates a ∼120 kDa trypsin-resistant glycopeptide that can be detected with PAS or PAS-silver staining. The glycopeptide quantitatively binds to Con A agarose and changes its gel mobility upon α-mannosidase treatment. PAS, PAS-staining of ExDG after trypsin digestion. Other lanes show PAS-silver staining: Input, amount control for the ExDG tryptic glycopeptide used for binding to lectin agarose beads; ConA, WFA, VVA, the glycopeptide bound to Con A, WFA, and VVA beads, respectively; α-Mannase “-” and “+”, α-mannosidase treatment of the glycopeptide with heat-inactivated (control) and active α-mannosidase, respectively. Note that PNGaseF-treated ExDG was used.