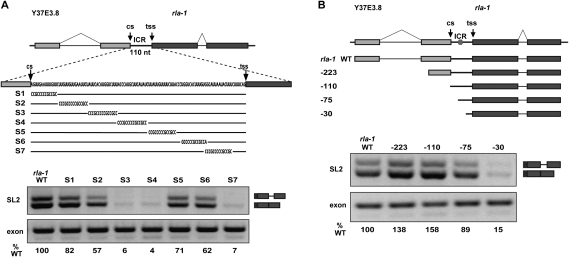
Figure 2.
A pre-mRNA region required for SL2 trans-splicing. (A, top) Diagram of in vitro splicing substrates and substitution mutations within the ICR of the rla-1 substrate RNA. (Bottom) RT–PCR of in vitro splicing reactions. SL2 trans-spliced products are indicated in the diagram at the right. (%WT) Ratio of the values of the experimental to the wild-type SL2 PCR products, each normalized to their respective exon PCR products. (B, top) Diagram of in vitro splicing substrates. The 5′ ends of each progressively shortened construct are indicated. Nucleotide distances upstream of the trans-splice site are −223, −110, −75, and −30 (wild type is −604). (Hexagon) Approximate location of S3/S4 element from A. (Bottom) RT–PCR of in vitro splicing reactions.