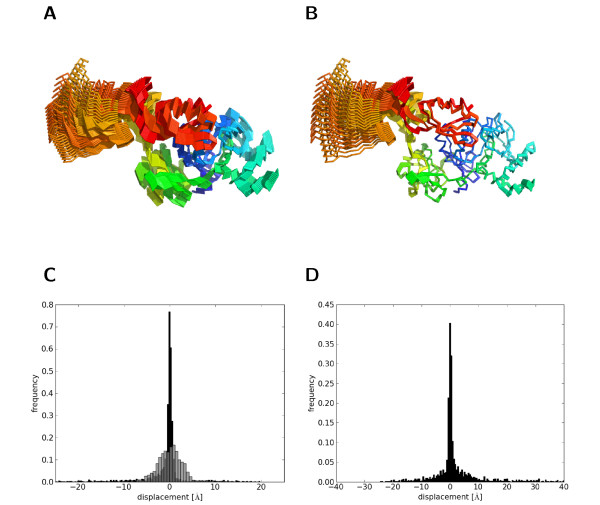
Figure 1.
Structural changes viewed from different frames of reference. A: Conformations of elongation factor G sampled along the first principal component. Conformations are optimally superimposed according to RMSD because they are generated in the Eckart frame. B: The core-weighted fit aims to superimpose the structurally invariant part, irrespective of the underlying physical mechanism. Viewed from this frame of reference most of the changes happen in the C-terminal domains (domain IV and V). C: Empirical distribution of the displacements in the Eckart frame (grey) and according to the core-weighted fit (black). D: Distribution of the displacements relating the bound and unbound structure of GroEL.