Fig. 2.
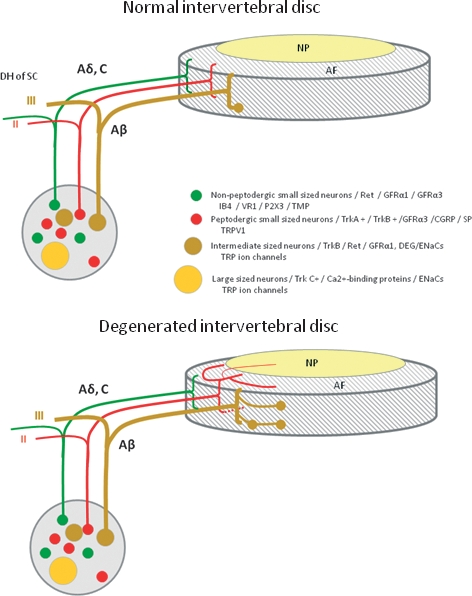
Schematic representation of the innervation of normal (top) and degenerated (bottom) intervertebral discs (IVDs), as well as the origin of sensory nerve fibers that innervate them. In the normal IVD, innervation is restricted to the outer layers of the annulus fibrosus (AF) and consists of small nerve fibers (red and green) and some large fibers forming mechanoreceptors (brown). In the degenerated IVD, nerve fibers are increased in number and they enter the inner layers of the AF and even the nucleus pulposus (NP). Furthermore, in these conditions, the density of mechanoreceptors in the superficial layers of IVDs is increased. Dorsal root ganglia (DRGs) contain different types of sensory neurons that project to the IVD and to the dorsal horn of the spinal cord (DH of SC). Thin myelinated Aδ fibers and unmyelinated C fibers arise from small neurons (red and green), which, in the spinal cord, synapse in lamina I and II and mediate nociception. The myelinated Aβ fibers (brown) arise from intermediate neurons; at the periphery they form slowly and rapidly adapting low-threshold mechanoreceptors, and synapse in lamina III and IV in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord; they mediate sensations of touch, pressure and vibration. Most of the sensory nerve fibers innervating the IVD are Aδ or C fibers. They originate from small peptidergic neurons expressing TrkA/TrkB (the receptor for nerve growth factor/brain-derived neurotrophic factor; red) or non-peptidergic neurons expressing the common signaling receptor for glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor family of neurotrophic factors (Ret) (red). Neurons in DRGs can be differentiated based on their pattern of expression of receptors for neurotrophic factors, pattern of expression of different ion channels primarily of the degenerin/epithelial sodium channels (DEG/ENaCs) (ENaCα, β and γ; acid-sensing ion channel (ASIC)1, ASIC2 and ASIC3) and transient receptor potential (TRP) (TRPA1, TRPC1, TRPC6 and TRPV1-4) families, and peptide content. CGRP, calcitonin gene-related peptide; GFRα1 and GFRα3, glial cell-line-derived neurotrophic receptor subtypes α1 and α3; P2X3, ATP-gated ion channel subtype P2X3; SP, substance P; TMP, thiamine monophosphatase; VR1, vanilloid receptor subtype 1.
