Figure 1.
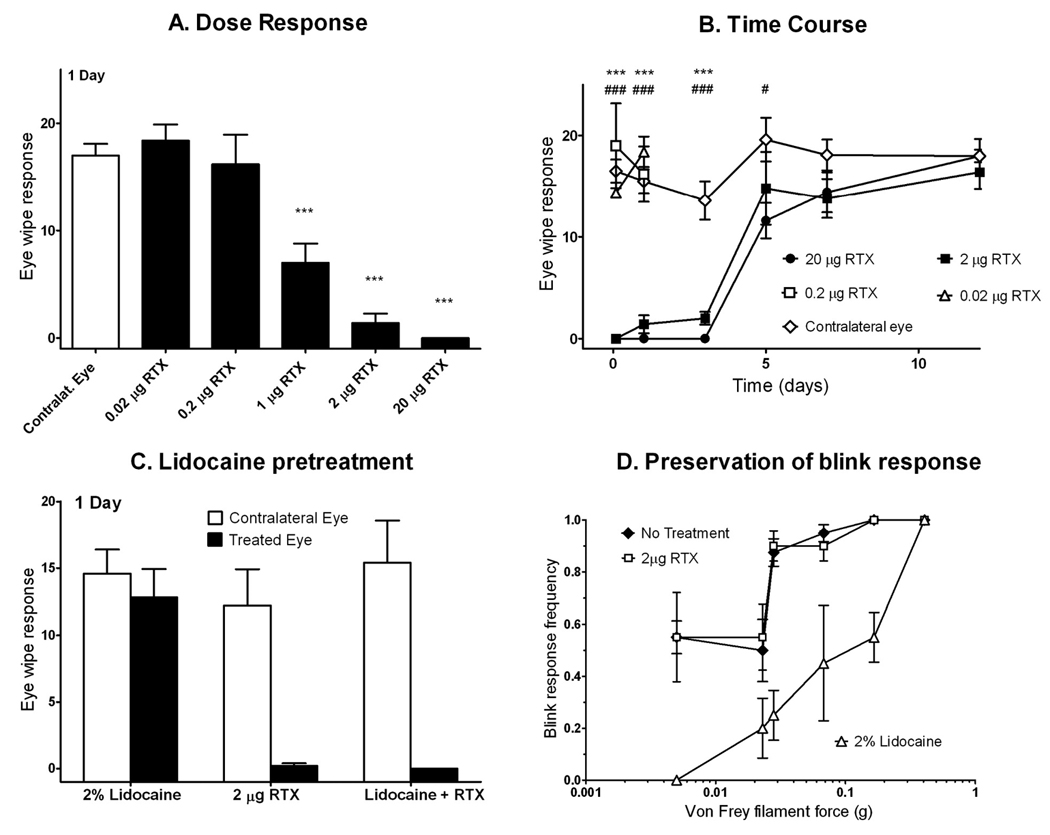
RTX suppression of CAP eye wipe response 1 day after treatment was dose-dependent (A). Doses of 0.02 and 0.2 µg had no significant effect, while doses of 1 µg and above reduced or eliminated eye wipe response. Stars indicate statistical difference from the contralateral eye using a paired t-test; number of stars indicates the p-value (one star, p<0.05; 2 stars, p<0.01; 3 stars, p<0.001). A single dose of RTX applied to the corneal surface ablates the eye wipe response to 0.02% CAP for several days (B). Contralateral eyes received no treatment prior to the CAP eye wipe test. By day 7, response in RTX-treated eyes normalized. Animals treated with 0.02 and 0.2 µg RTX were only assessed at 2 hr and 1 day, as no effect was observed. As determined by 2-way ANOVA, stars indicate statistical difference between 2 µg RTX and vehicle and pound signs indicate statistical difference between 20 µg RTX and vehicle. Lidocaine pretreatment does not interfere with RTX therapeutic action (C). Animals received RTX alone, lidocaine alone, or lidocaine pretreatment 5 to 10 minutes prior to RTX (n=5 per group). The eye wipe test was performed one day later. RTX suppressed eye wipe response, both with and without lidocaine pretreatment. Lidocaine alone had no effect on eye wipe response 24 hr after application. Lidocaine did blunt the nociceptive stimulation that occurred with acute application of RTX. Treatment with 20 µg RTX spares corneal blink response to mechanical stimulation with von Frey hairs (D). 20 µg RTX or 20 µL 2% lidocaine was applied topically onto the cornea 24 hr and 10 min, respectively, before testing, with the contralateral eye receiving no treatment (n=4 per group). Von Frey hairs were touched to the corneal surface to assess blink response. Each hair was touched 5 times to each eye. RTX had no significant effect on the sensitivity of blink response, while lidocaine significantly suppressed response.
