Figure 5.
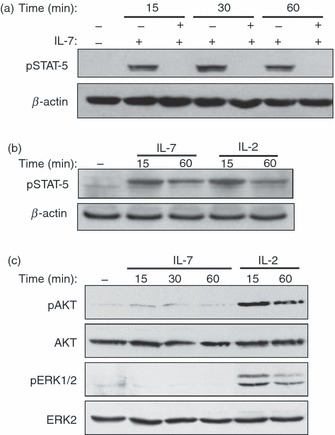
Activation of Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT), AKT and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) by interleukin-7 (IL-7) in human effector/memory T cells. (a) IL-7 activates the JAK/STAT signalling pathway. Human effector/memory T cells cultured under deprived conditions were stimulated or not with IL-7 (2 ng/ml) for different periods of time in the presence or absence of the Pan-JAK inhibitor. Non-stimulated cells (−) were maintained in medium alone for 1 hr. Activation of STAT5 was determined by immunoblot analysis using specific antibody that recognizes the phosphorylated form of STAT5. The blot was stripped and re-probed with anti-β-actin monoclonal antibody to ensure equal loading. (b) The cells were activated as in (a) with IL-7 or with IL-2 (50 U/ml) and STAT5 phosphorylation was determined by immunoblot analysis. (c) IL-7 is a weak activator of AKT and ERK in human effector/memory T cells. The cells were activated under deprived conditions with IL-7 for different periods of time. Non-stimulated cells (−) were maintained in medium alone for 1 hr. In some cases, the cells were also activated with IL-2 (50 U/ml) as indicated. AKT and ERK activation was determined by immunoblot analysis using antibodies that recognize the phosphorylated forms of AKT and ERK1/2. The blot was stripped and re-probed with anti-ERK2 and anti-AKT antibodies to ensure equal loading. The results in (a) and (c) and in (b) are respectively representative of five and three independent experiments performed with T cells from different blood donors.
