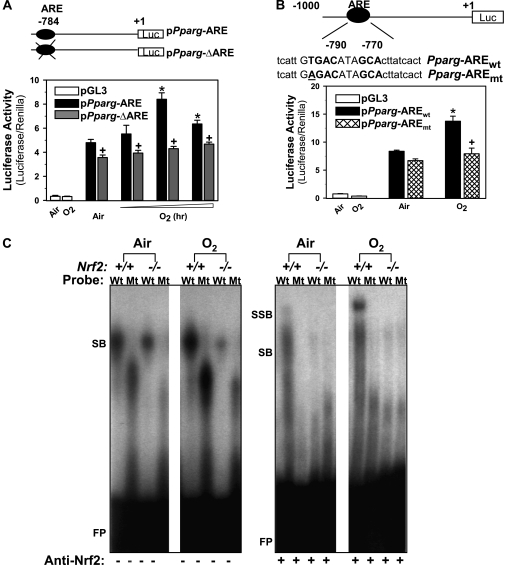
Figure 3.
Functional assessment of a putative antioxidant response elements (ARE) on -784 region of Pparg promoter. (A) Transactivating activity of -784 ARE sequence was determined by promoter deletion analysis. Nrf2 overexpressing airway epithelial cells (BEAS-2B) were prepared by transfection with murine Nrf2 expression vector (pFlag-Nrf2). The cells were then transfected by Pparg promoter-luciferase reporter constructs with (pPparg-ARE) or without (pPparg-ΔARE) -784 ARE region, and exposed to either air or hyperoxia (4–12 h). Mean ± SEM. presented (n = 6–9/group). * = significantly higher than air exposure under same transfection condition (P < 0.05). + = significantly lower than exposure-matched pPparg-ARE transfection (P < 0.05). (B) Transactivating activity of -784 ARE sequence was further determined by mutation analysis. Briefly, BEAS-2B cells overexpressing Nrf2 were transfected with a vector containing wild-type Pparg promoter bearing -784 ARE (pPparg-AREwt) or a vector containing the promoter with a mutation in -784 (pPparg-AREmt) incorporated by site-directed mutagenesis. The cells were then exposed to either air or hyperoxia (12 h). * = significantly higher than air exposure under the same transfection condition (P < 0.05). + = significantly lower than exposure-matched pPparg-AREwt (P < 0.05). (C) Gel shift analysis was performed on an aliquot of lung nuclear proteins from Nrf2+/+ and Nrf2−/− mice exposed to air or O2 (48 h) using γP32-end labeled wild-type (Wt; tcattGTGACataGCActtatcact) or mutated (Mt; tcattGGTACataGCActtatcact) -784 ARE-like probe. Hyperoxia increased Wt probe binding activity of nuclear proteins from Nrf2+/+, but not those from Nrf2−/− mice. Hyperoxia-induced increase of total DNA binding and specific Nrf2 binding (+ anti-Nrf2 antisera) was detected only on Wt probe by nuclear proteins from Nrf2+/+ mice. FP = free probes; SB = shifted bands; SSB = super shifted bands.