Figure 4.
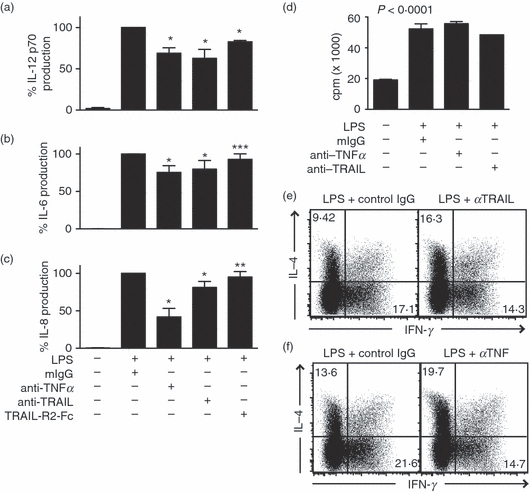
Tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) neutralization impairs lipopolysaccharide (LPS) -induced cytokine production and dendritic cell (DC) -driven T-cell differentiation into interferon-γ (IFN-γ) -producing effectors. TRAIL or tumour necrosis factor (TNF) neutralization partially inhibits LPS-induced production of (a) interleukin-12 (IL-12), (b) IL-6 and (c) IL-8 by DCs. Cytokine production was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay 24 hr after stimulation with LPS and the indicated immunoglobulin G antibodies. The samples treated with LPS and control IgG were normalized as 100%. Results represent the average from five experiments using DCs derived from different donors (mean ± SEM). The ranges of cytokine production from different donor cells were: IL-12 (6–32 pg/ml); TNF (349–992 pg/ml); IL-8 (87–216 pg/ml); IL-6 (398–695 pg/ml). *P < 0·0001, **P < 0·05 and ***P = 0·256 because of one outlier that exhibited 20% increase in IL-8 production compared with LPS + mIgG control. (d) DC-induced allogeneic T-cell proliferation was not affected by TRAIL or TNF neutralization. Five days after co-culture with DCs stimulated with the indicated treatments, T cells were pulsed with [3H]thymidine for 20 hr to measure T-cell proliferation (mean ± SEM). (e,f) Neutralization of (e) TRAIL or (f) TNF partially inhibits the DC-driven development of IFN-γ-producing effector T cells. DCs stimulated with LPS in the presence of neutralizing antibody against TRAIL, TNF or control IgG were washed and co-cultured with allogeneic CD4+ T cells as described in the Methods. IFN-γ and IL-4 production were determined by intracellular staining and fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis. The numbers represent the percentages of cells in the respective quadrants. Results are representative of six experiments with cells derived from different donors.
