Figure 2.
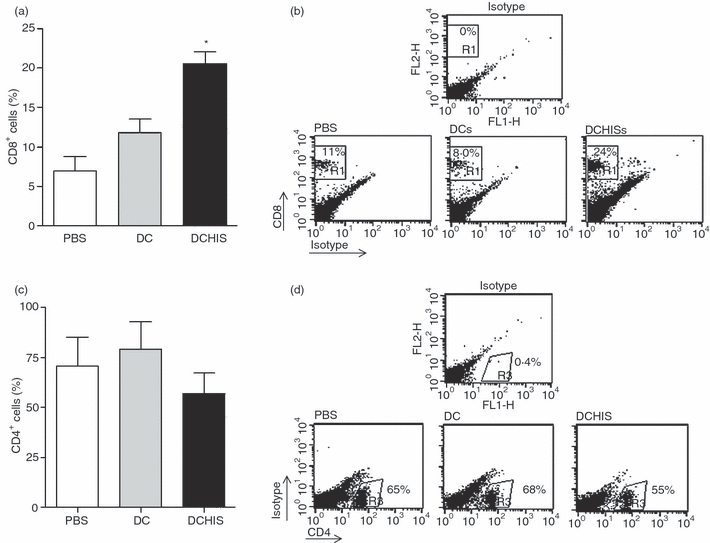
Histamine-pretreated dendritic cells (DCs) stimulate the recruitment of CD8+ T lymphocytes in the lungs of allergic mice. BALB/c mice were inoculated intraperitoneally (i.p.) with ovalbumin (OVA) on days 0 and 7. On day 14, sensitized mice were challenged intranasally with OVA for 5 days. Then, DCs obtained from bone marrow precursors, pretreated or not with 1 μm histamine (30 min at 37°) and pulsed with 100 μg/ml OVA (3 hr at 37°), were injected intratracheally (i.t.) (5 × 105 cells/mouse). Control mice were injected with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). After 7 days, mice were killed and the lungs were processed. Lung T cells were purified using anti-CD3 antibodies coupled to magnetic beads. Purified T cells were stained with phycoerythrin (PE)-labelled anti-CD8 antibodies and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labelled anti-CD4 antibodies. Cells were analysed by flow cytometry. (a, c) Results are expressed as the percentage of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells, respectively, and represent the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) for eight experiments. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (*P ≤ 0·01) versus controls (PBS). (b, d) Representative dot-plots (n = 8) are shown.
