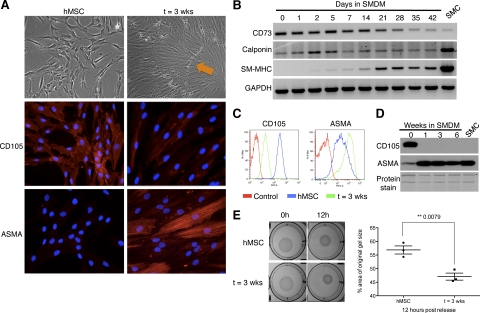
Figure 1.
Cells derived from SM differentiation of hMSCs reproduce the phenotypic and molecular characteristics of mature SMCs. A: Brightfield images (×100 magnification) and immunofluorescence for CD105 and α-smooth muscle actin (ASMA) in human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSC) and after SM differentiation (t = 3 weeks) (×200 magnification). Characteristic ‘hills (orange arrow) and valleys’ are observed by day 21. B: RT-PCR analysis of CD73, calponin, and smooth muscle myosin heavy chain (SM-MHC) during SM differentiation. GAPDH is used as RNA loading control. SMC: RNA from smooth muscle tissue used as a control. FACS (C) and Western blot (D) analyses of CD105 and ASMA during SM differentiation. For FACS, an isotypic control for each respective antibody is used to detect nonspecific staining (Control). SMC: protein lysate of smooth muscle cells isolated from human myometrial tissue. Amido black (protein staining) serves as loading control. E: Gel-contraction assay on hMSCs maintained in MSC medium (hMSC) or smooth muscle differentiation medium (t = 3 weeks), visualized at 0 hours and 12 hours post release (pictures, left); differences in contraction quantified at 12 hours (right). Image J software was used to measure the area of the gel and of the well, which was used for normalization.