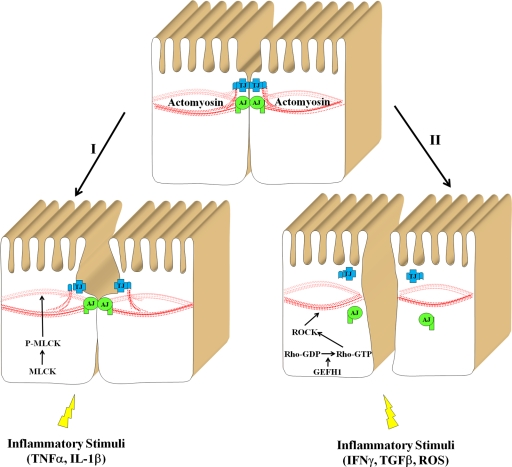
Figure 3.
Signaling pathways that mediate actomyosin-dependent disruption of the epithelial barrier in inflammation. Two signaling pathways that are activated by different inflammatory stimuli and result in disruption of the epithelial barrier are presented. The first pathway involves activation of MLCK resulting in a modest contraction of perijunctional actomyosin belt and reversible increase in paracellular permeability without gross alterations in AJC structure. The second pathway involves activation of the GEF-H1-Rho-ROCK pathway that leads to profound actomyosin contraction and AJC disassembly.