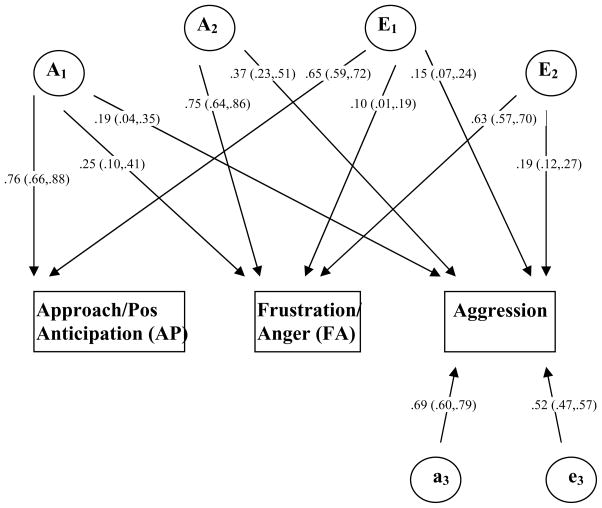
Figure 2.
Standardized path estimates for best fitting “AE” model. We used a multivariate Cholesky decomposition to partition the variances of, and covariances between, approach/positive anticipation (AP), frustration/anger (FA) and aggression, into genetic and non-genetic components. Latent variables represent overlapping additive genetic effects (A), additive shared environment effects (C), and additive nonshared environment effects including error (E), as well as residual genetic (a), shared environmental (c), and nonshared environmental (e) variance. Shared environment paths (C, c) are not shown, as they were fixed = 0 in the best fitting model because shared environment effects were negligible. The pathways between latent variables representing genetic variance or covariance across twins are set at 1 for monozygotic (MZ, identical) twins and .5 for dizygotic (DZ, fraternal) twins. The pathways for shared environmental variance or covariance across twins are set at 1 for MZ and DZ twins, whereas the pathways for nonshared environmental variance or covariance across twins are set at 0 for MZ and DZ twins.