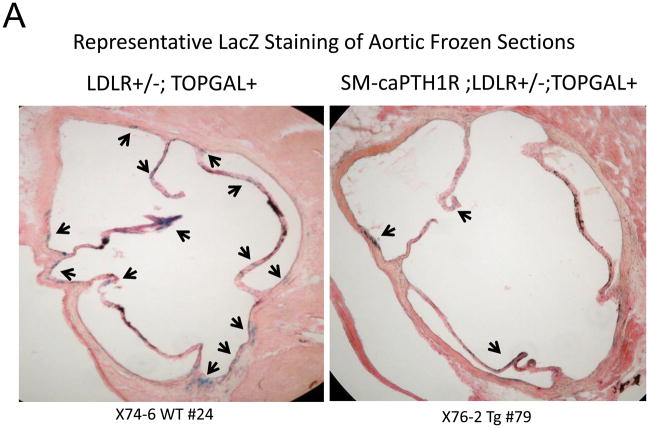
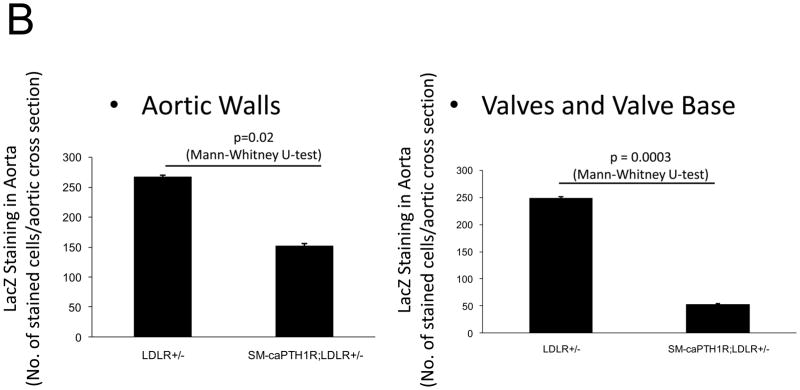
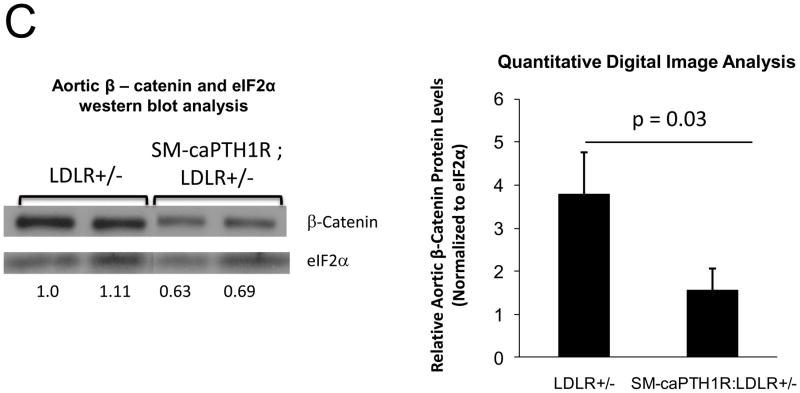
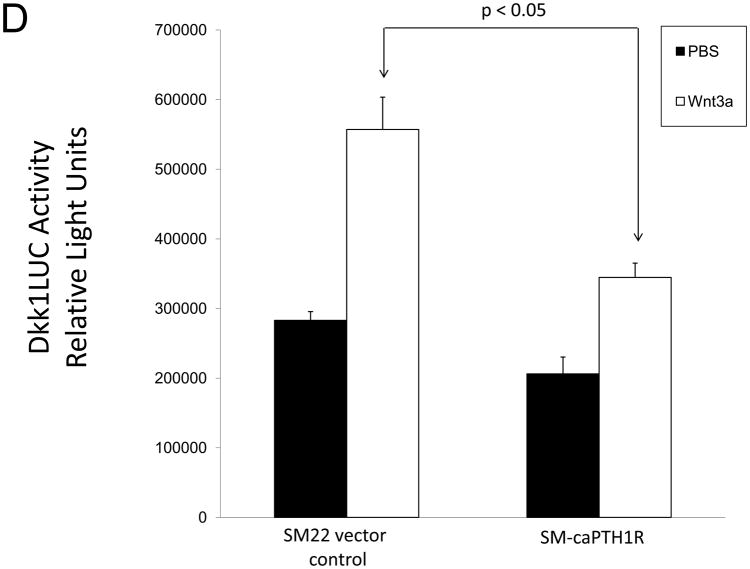
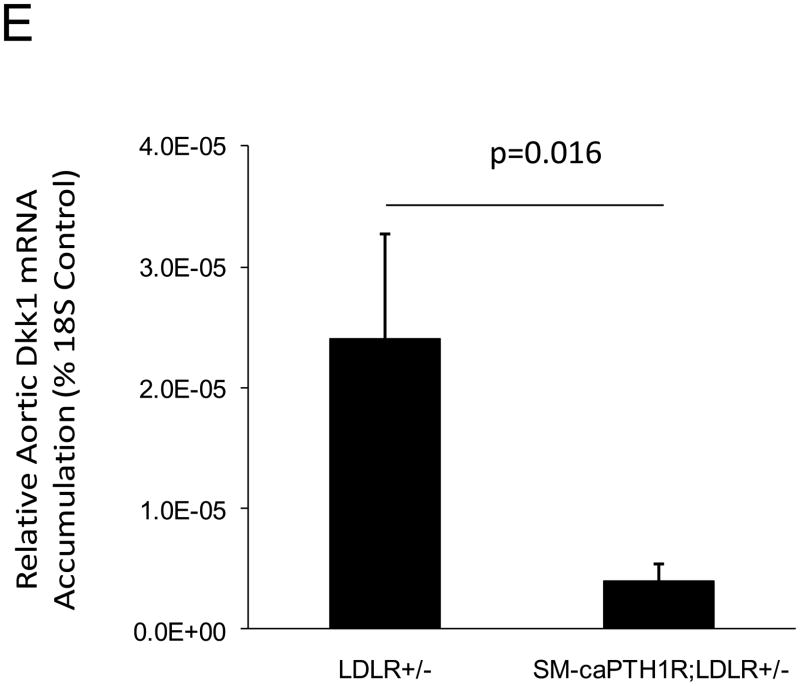
Figure 4. The SM-caPTH1R transgene reduces aortic β-catenin signaling and β-catenin protein accumulation in diabetic LDLR+/− mice.
SM-caPTH1R;LDLR−/− transgenic mice were bred with TOPGAL+;LDLR+/+ reporter mice, and the extent of aortic LacZ staining assessed in SM-caPTH1R;LDLR+/−;TOPGAL+ mice vs. LDLR+/−;TOPGAL+ siblings following 1.5 months of HFD challenge. Panel A, representative aortic LacZ reporter visualization by staining frozen sections from these cohorts. Panel B, the extent of LacZ staining was reduced in aortas of LDLR+/−;TOPGAL+ reporter mice possessing the SM-caPTH1R transgene (n = 12). Panel C, the accumulation of aortic β-catenin was reduced in LDLR+/− mice possessing the SM-caPTH1R transgene (n = 4). Panel D, Wnt-induced Dkk1 promoter activity is inhibited by SM-caPTH1R in aortic VSMCs in vitro. Panel E, the expression of aortic Dkk1, an endogenous target of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, was reduced in vivo in mice possessing the SM-caPTH1R transgene (n = 12).