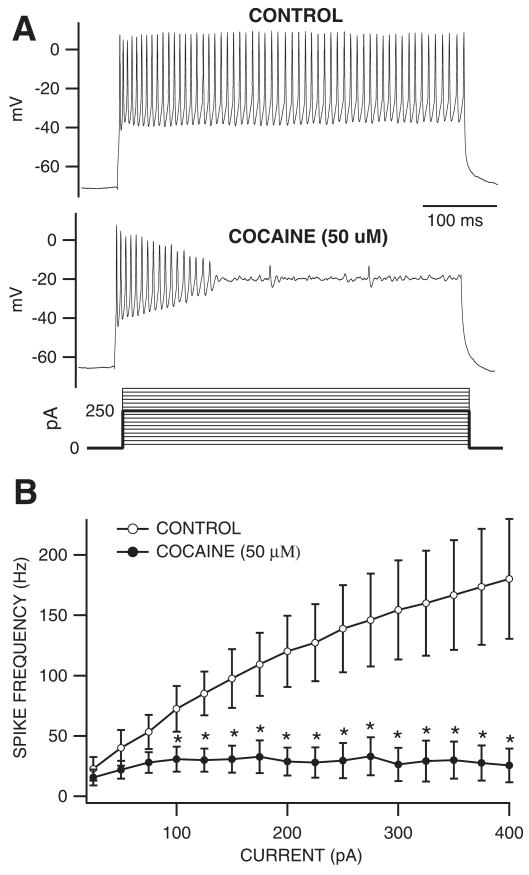
Fig. 4.
Cocaine reduced current-evoked spiking of VTA GABA neurons in vitro. (A) These are representative current-clamp traces of current-evoked VTA GABA neuron spikes recorded in the horizontal midbrain slice preparation. Note the lack of spike accommodation characteristic of VTA GABA neurons (Allison et al., 2006). Superfusion of cocaine (50 μm) markedly reduced spiking at this level of depolarization (250 pA; darker line of the current steps that were performed). (B) This graph summarizes the effects of 50 μm cocaine on the frequency of current-evoked spiking of VTA GABA neurons at all current steps tested (25–400 pA steps shown in A). Superfusion of cocaine significantly reduced spiking at current steps 100–400 pA in all cells tested. *P < 0.03 at each point.