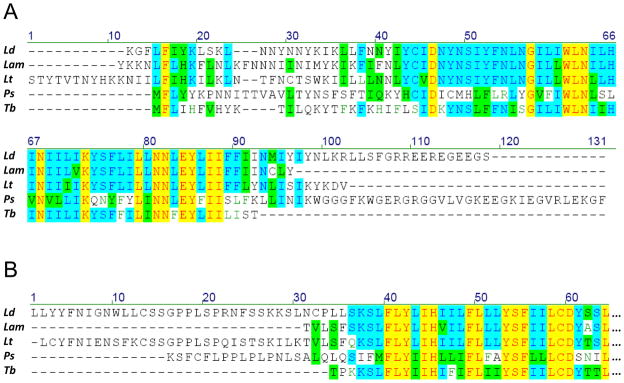
Fig. 1.
Comparison of MURF1 and MURF5 amino acid sequences from Leishmania mexicana amazonensis (Lam) with their homologs from Leishmania donovani (Ld), Leishmania tarentolae (Lt), Phytomonas serpens (Ps), and Trypanosoma brucei (Tb). Multiple sequence alignment was generated using Vector NTI. Identical residues found in a given position in all sequences are highlighted with yellow, and those in the majority of sequences are indicated with blue, while conservative substitutions are shown with green. Dashes represent alignment gaps: (A) multiple alignment of the complete predicted MURF5 sequences; (B); alignment of the N-terminal ends of the MURF1 sequences.