Fig. 3.
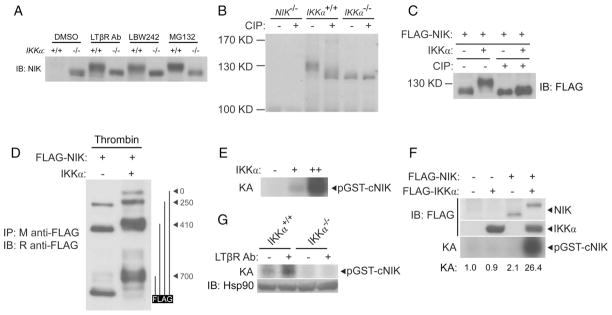
IKKα phosphorylates NIK. (A) NIK from IKKα−/− fibroblasts migrates further on SDS-PAGE gels than does NIK from IKKα+/+ fibroblasts regardless of the stimulus used to trigger its accumulation. Fibroblasts were treated for 4 hours with the indicated stimuli and the abundance of NIK was roughly equilibrated by loading different amounts of extract to facilitate migration analysis. (B) Differential migration of NIK from IKKα+/+ and IKKα−/− fibroblasts is due to phosphorylation. The accumulation of NIK was triggered with the proteasome inhibitor MG132, after which NIK was immunopurified and subjected to treatment with CIP. (C) IKKα leads to the phosphorylation of NIK in transfected HEK 293T cells. HEK 293T cells were cotransfected with plasmid encoding FLAG-tagged NIK alone or with plasmid encoding IKKα. Extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation with agarose conjugated to antibody against FLAG. Samples were split, and half were subjected to treatment with CIP. (D) IKKα-dependent phosphorylation of NIK is retained in the C-terminal 247 amino acid residues of NIK. An additional thrombin cleavage site at residue 700 of NIK was generated by means of a T702G/D703R mutation of the protein. HEK 293T cells were cotransfected with plasmid encoding NIK, FLAG-tagged at the C terminus, with or without plasmid encoding IKKα. FLAG-NIK was immunopurified, subjected to partial digestion with thrombin, and analyzed by Western blotting with polyclonal rabbit antibody against FLAG. Potential thrombin cleavage products are shown on the right. (E) IKKα phosphorylates the C terminus of NIK. In vitro kinase assay (KA) of the GST-cNIK(700–942) substrate with increasing amounts of immunopurified IKKα from HEK 293T cells. (F) Addition of NIK substantially enhances the IKKα-dependent phosphorylation of the C terminus of NIK. HEK 293T cells were transfected as indicated; lysates were immunopurified with M2-conjugated agarose and subjected to kinase assay (KA). (G) Endogenous IKKα phosphorylates the C terminus of NIK in a signal-dependent manner. IKKα+/+ or IKKα−/− fibroblasts were treated for 3 hours with an agonistic antibody against LTβR (2 μg/ml). Lysates were immunoprecipitated with an antibody against IKKα and subjected to KA.