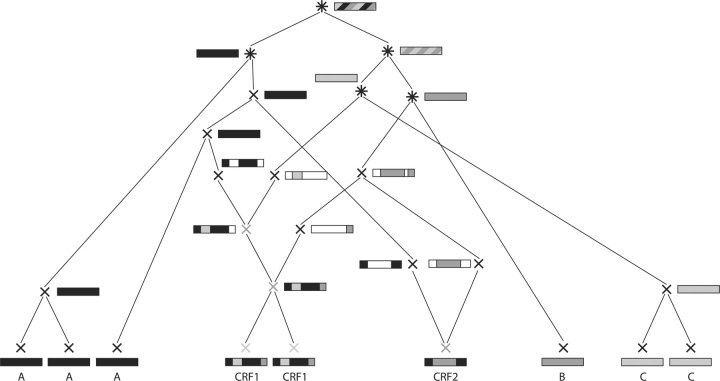
Fig. 2.
A legal ARG corresponding to the classification given in Figure 1. At the bottom, the nine input (tip) sequences with their classification are shown. The tip sequences are defined to be generated at time zero. Looking from bottom to top (i.e. into the past), two nodes coalescing to one (parental) node, represent the event of these two nodes finding their most recent common ancestor. A node splitting into two parental nodes represents a recombination event. Single-color boxes show the subtype of the node. Horizontally segmented boxes show for a recombinant sequence the parental subtypes of each segment. Diagonally shaded boxes show the different subtypes the node belongs to. White parts in boxes indicate positions not contributing to the tip sequences and, hence, of which we do not keep track. For recombination events, they also illustrate the positions of the recombination breakpoints. For further details, see Section 2.3.