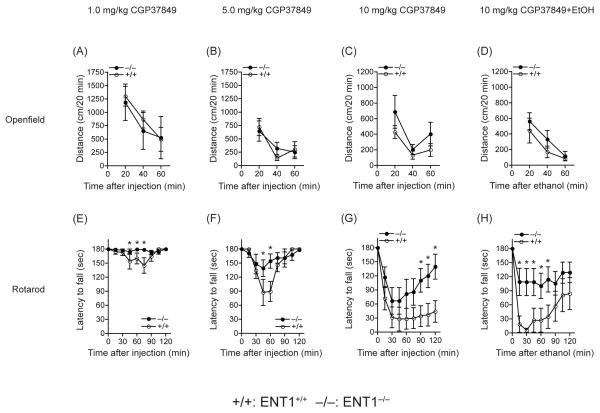
Figure 1.
Effect of an NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist (CGP37849) on ethanol-induced locomotion and ataxia in ENT1−/− mice (−/−). (A-C) Locomotor activity was similar between genotypes in response to 1.0, 5.0 or 10 mg/kg CGP37849. (D) Ethanol-induced locomotion in response to CGP37849 was also similar between genotypes. (E-G) CGP37849 induced significant ataxic effects at 1.0, 5.0 or 10 mg/kg doses. (H) The ataxic effect of 1.0 g/kg ethanol 15 min following an NMDA receptor antagonist (CGP37849; 10 mg/kg, i.p.) was measured using a rotarod. ENT1−/− mice (n = 10) are less intoxicated than ENT1+/+ littermates (+/+; n = 7) (*p < 0.05 compared to ENT1+/+ mice by Tukey tests). Data are presented as mean ± SEM.