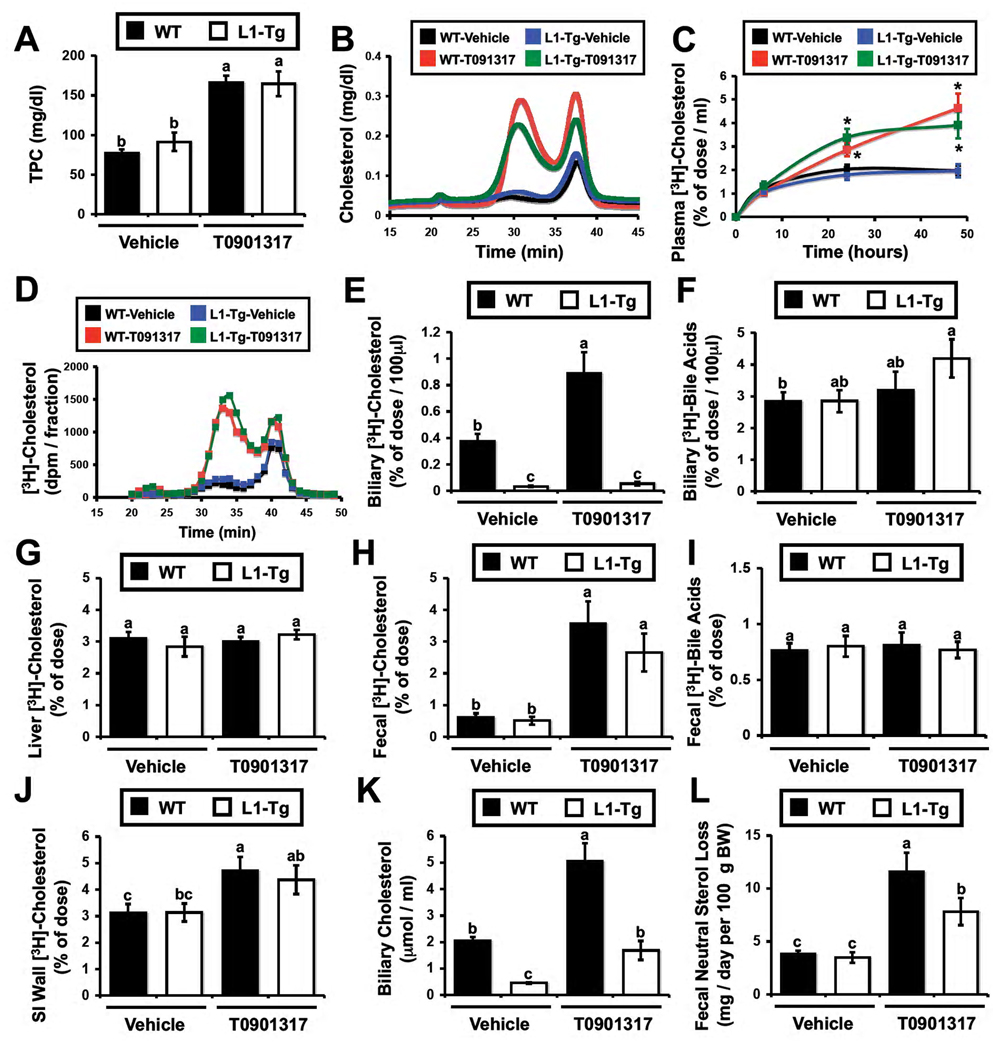
Figure 2. Macrophage RCT is normal in mice genetically engineered to lack the ability to secrete cholesterol into bile.
Wild type mice (■ in bar graphs) or NPC1L1-LiverTg (□ in bar graphs, L1-Tg) littermates were maintained on a standard chow diet in the absence (Vehicle) or presence of the LXR agonist T0901317 (25 mg/kg per day) for 7 days. During the last 48 hours, mice were singly housed and macrophage to feces RCT was measured as described in the materials and methods.
(A) Total plasma cholesterol (TPC) levels.
(B) Mass cholesterol distribution of pooled plasma (n=4 per pool).
(C) Time course of [3H]-cholesterol recovery in plasma; * = significantly different than WT-vehicle group within each time point, P < 0.05.
(D) [3H]-cholesterol distribution of pooled plasma (n=4 per pool).
(E) [3H]-cholesterol recovery in newly secreted bile.
(F) [3H]-bile acid recovery in newly secreted bile.
(G) [3H]-cholesterol recovery in the liver.
(H) [3H]-cholesterol recovery in the feces.
(I) [3H]-bile acids recovery in the feces.
(J) [3H]-cholesterol recovery in the small intestine (SI) wall.
(K) Mass biliary cholesterol concentrations in newly secreted bile.
(L) Mass fecal neutral sterol loss. Results are combined from two independent experiments. Data in panels A,C,E,F,G,H,I and J represent the means ± SEM from 7–11 mice per group, and data in panel K and L represent means ± SEM from 5–9 mice per group. Means not sharing a common superscript differ significantly, P < 0.05.