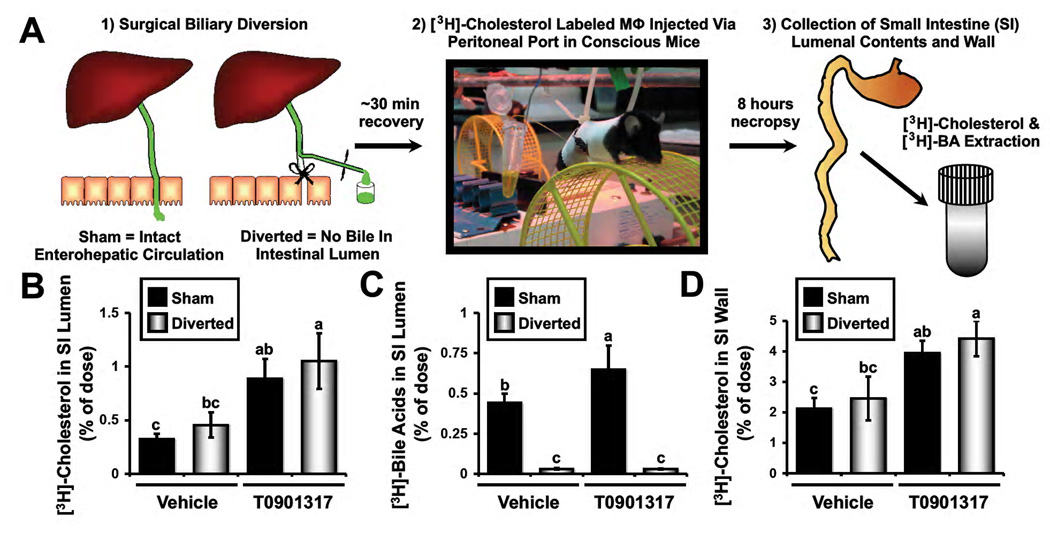
Figure 3. Surgical biliary diversion reveals the existence of a non-biliary pathway for macrophage RCT.
Wild type C57BL/6N mice were maintained on a standard chow diet in the absence (Vehicle) or presence of the LXR agonist T0901317 (25 mg/kg per day) for 7 days.
(A) Experimental design: Following 7 days of vehicle or LXR agonist treatment, mice were either sham operated or underwent complete surgical bile diversion as described in materials and methods. Thereafter, mice received a [3H]-cholesterol labeled macrophage (Mϕ) dose via an externalized peritoneal port in order to ensure no dose was accidentally injected into the intestine. After 8 hours, the small intestinal (SI) lumenal contents and wall were collected, and extracted to separate [3H]-cholesterol and [3H]-bile acids.
(B) [3H]-cholesterol recovered in the SI lumenal contents.
(C) [3H]-bile acids recovered in the SI lumenal contents.
(D) [3H]-cholesterol recovered in the SI wall. Data represent the means ± SEM from 5–9 mice per group, and means not sharing a common superscript differ significantly, P < 0.05.