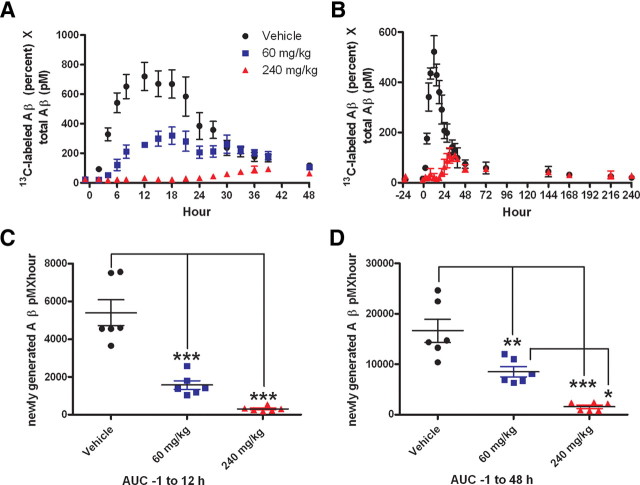
Figure 6.
Newly generated Aβ was reduced in response to GSI treatment in the CNS of rhesus monkeys (n = 6). A, C, D, In a crossover study, male rhesus monkeys (n = 6) were infused with 13C6-leucine (4 mg/kg/h) for 12 h, and treated with vehicle (black circle), 60 mg/kg GSI (blue square), or 240 mg/kg GSI (red triangle). B, In an extended study (n = 6, 3/group), animals were treated with vehicle or 240 mg/kg GSI. A, B, Generation of new Aβ was partially blocked with administration of 60 mg/kg, and nearly completely blocked at the 240 mg/kg dose as indicated by the dose-dependent decrease in the amount of 13C6-leucine-labeled Aβ (LC-MS). C, D, AUC analysis of newly generated Aβ indicates that the means of newly synthesized Aβ are significantly reduced by GSI treatment during the leucine infusion (0–12 h) (C) and levels do not recover within 48 h (D), as assessed by a repeated measures 1-way ANOVA (p < 0.0001) and post hoc analysis (Tukey) (*p = 0.01 to 0.05;**p = 0.001 to 0.01; ***p < 0.001). Error bars indicate SEM.