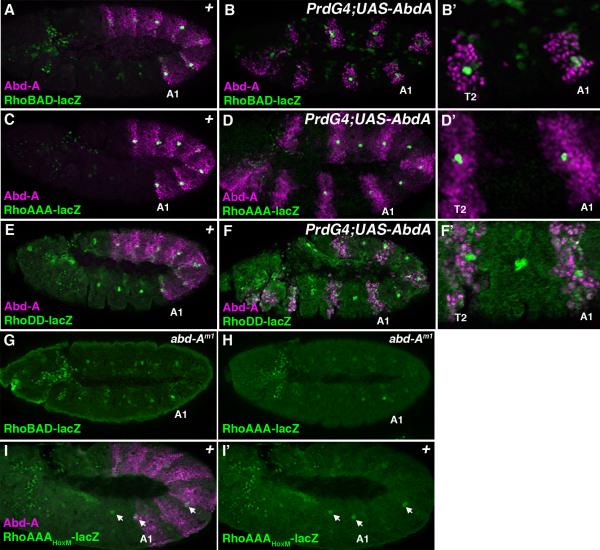
Figure 2. Hox dependent and Hox-independent regulation of Rho enhancer activity.
Lateral views of stage 11 Drosophila embryos immunostained for β-gal (green) and Abd-A (purple). The first abdominal segment (A1) of each embryo is noted. A. A RhoBAD-lacZ embryo reveals higher β-gal levels in abdominal than thoracic SOP cells. B-B’. A PrdG4;UAS-Abd-A;RhoBAD-lacZ embryo reveals the induction of thoracic β-gal to abdominal levels within the T2 thoracic segment expressing Abd-A protein. Close-up view of the T2, T3, and A1 segments is shown at right. C. A RhoAAA-lacZ embryo reveals high β-gal levels in the abdominal C1 SOP cells. D-D’. A PrdG4;UAS-Abd-A;RhoAAA-lacZ embryo reveals the induction of thoracic β-gal to abdominal levels within the T2 thoracic segment expressing Abd-A protein. Close-up view of the T2, T3, and A1 segments is shown at right. E. A RhoDD-lacZ embryo reveals low equal β-gal levels in both the thoracic and abdominal C1 SOP cells. F-F’. A PrdG4;UAS-Abd-A;RhoDD-lacZ embryo reveals that ectopic Abd-A has no affect on β-gal levels within either the thorax or abdomen. Close-up view of the T2, T3, and A1 segments is shown at right. G. A abd-Am1;RhoBAD-lacZ embryo reveals low β-gal levels in both abdominal and thoracic segments. H. A abd-Am1;RhoAAA-lacZ embryo reveals low β-gal levels in both abdominal and thoracic segments. I. A RhoAAAHoxM-lacZ embryo reveals sporadic low β-gal levels (arrows) in both abdominal and thoracic segments.