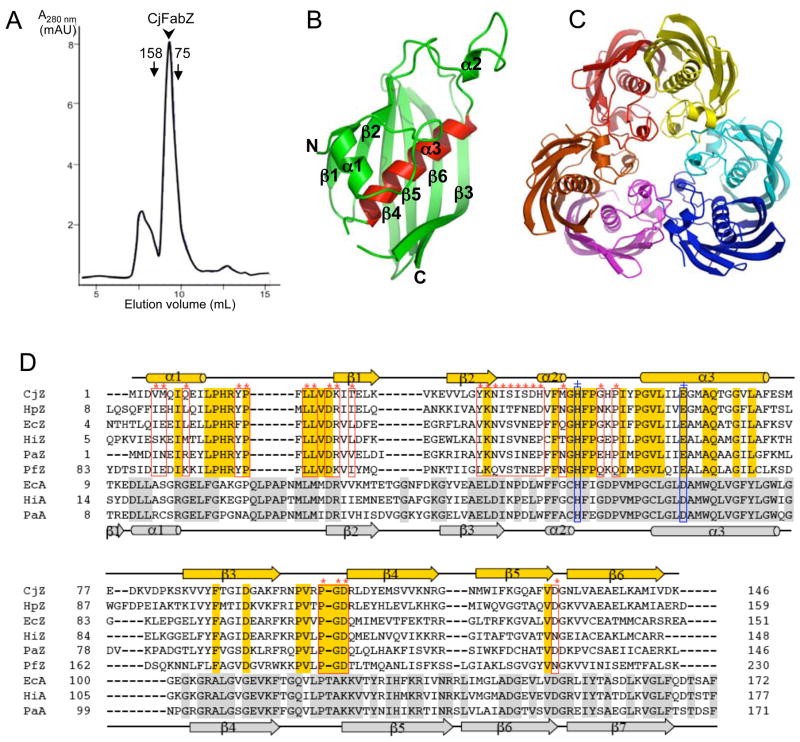
Figure 2. Structure of CjFabZ.
(A) Analytical gel filtration chromatograph. The purified CjFabZ protein eluted as a hexamer, with an estimated molecular mass of 100 kDa. (B) Ribbon diagram of the CjFabZ monomer structure. The secondary structures are labeled. N and C denote the N and C termini of CjFabZ, respectively. The central helix (α3) is highlighted in red. (C) Ribbon diagram of the CjFabZ hexamer in the asymmetric unit. The view is from the 3-fold axis of the hexamer. The dimer A/B is colored in red/yellow, the dimer C/D in cyan/blue, and the dimer E/F in magenta/orange. (D) Structure-based sequence alignment of FabZ and FabA. Secondary structures are indicated above and below the primary sequences for FabZ and FabA, respectively. Identical residues are highlighted with gold and silver boxes, for FabZ and FabA, respectively. In FabZ, residues involved in the formation of the hexamer (trimer of dimers) are indicated with red boxes (*). The conserved catalytic residues, His and Glu/Asp, are indicated with blue boxes (+).