Figure 3. Active site of CjFabZ.
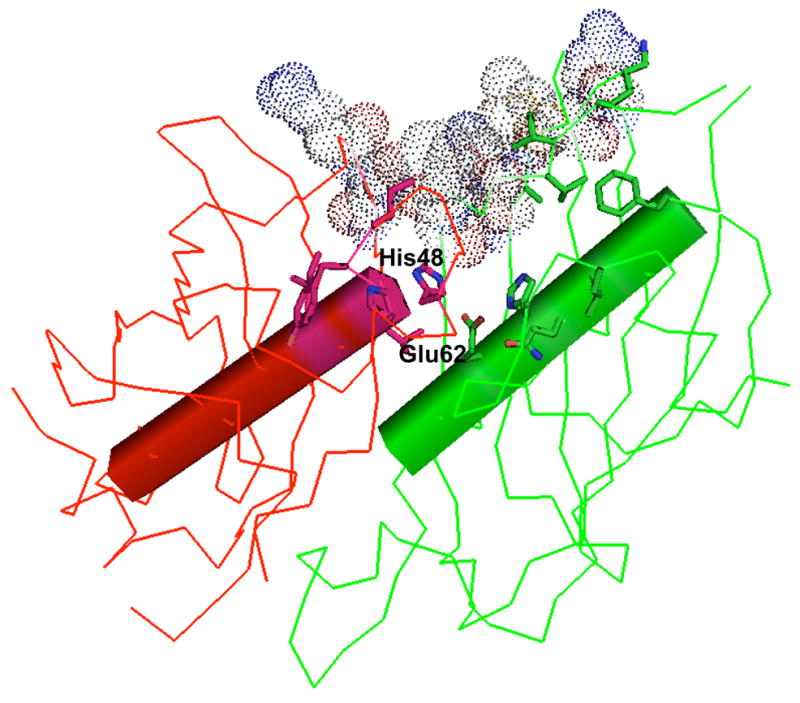
The active sites of CjFaZ were defined by analysis of other known FabZ structures. For clarity, only one active site is depicted. Key amino acid residues forming the substrate-binding tunnel are shown in stick model, and catalytic residues are labeled. The proposed ACP-interaction site is depicted in CPK model.
