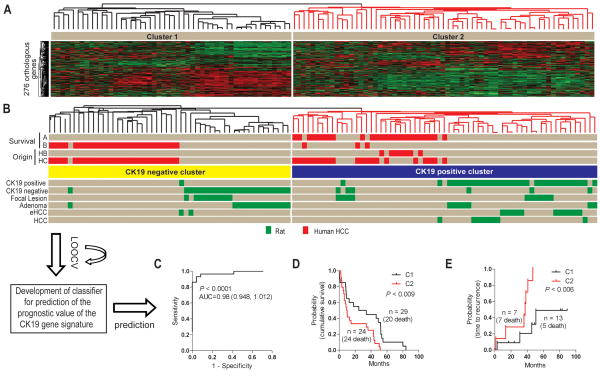
Figure 6.
The prognostic power of the CK19 gene signature. (A) The HCC data set was generated from a cohort of 53 HCCs obtained from Caucasian and Chinese patients and hybridized to illumina bead chips. A list of 276 orthologous genes between the two species presented on both platforms was identified. (B) Comparative functional genomics. The CK19 gene signature separates the human HCC according to the previous A and B sub-classification. Individual human and rat samples are shown in red and green, respectively. (C) Development of a gene classifier for prediction of the prognostic value of the CK19 gene signature. A Bayesian compound covariate prediction analysis showed a probability of 0.98 for correct classification. The probability is represented by the area under the ROC curve (AUC). To build a classifier, a class random variance model was used to identify genes univariately significant at α≤0.001. Seven different algorithms were used in the prediction of the correct classification during LOOCV with a prediction rate 89 to 98%. The performance of the classifier estimating the correct classification in each of the prediction models is given in supplementary table 4. (D, E) Cumulative survival. Integration and cluster analysis identified clinically relevant distinct subgroups of human HCC based on the CK19 gene expression signature. Kaplan-Meier plots and Mantel-Cox statistical analysis were applied in the survival analysis.